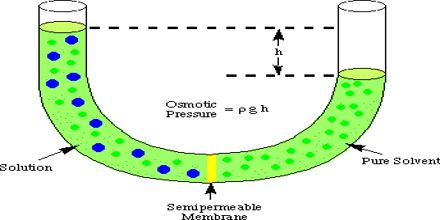
 The more water moving across the membrane, the higher the osmotic pressure. Osmosis process refers to the movement of solvent molecules through a membrane from a segment with low concentration is low to the segment with the high concentration. What is the relationship between TDS and osmotic pressure? Hence, results are obtained in a very short time. To calculate osmotic pressure, use the following formula: Spell. The lowest force per unit of area, i.e. View the full answer. Osmotic pressure can be thought of as the pressure that would be required to stop water from diffusing through a barrier by osmosis.
The more water moving across the membrane, the higher the osmotic pressure. Osmosis process refers to the movement of solvent molecules through a membrane from a segment with low concentration is low to the segment with the high concentration. What is the relationship between TDS and osmotic pressure? Hence, results are obtained in a very short time. To calculate osmotic pressure, use the following formula: Spell. The lowest force per unit of area, i.e. View the full answer. Osmotic pressure can be thought of as the pressure that would be required to stop water from diffusing through a barrier by osmosis. 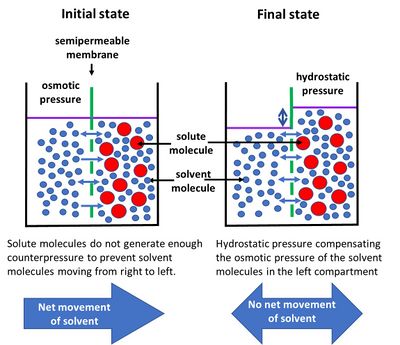 This property is dependent upon the concentration of the solute particles present in solution and hence is one of the colligative properties. Osmotic pressure is the same everywhere of the liquid, thus it is calculated considering the whole system. There will be an escape of water and solute into the interstitial space resulting in interstitial edema whenever the hydrostatic In patients with low oncotic pressure, fluid will tend to accumulate in the tissues, resulting in edema. 2. Osmotic pressure is the pressure created by water moving across a membrane due to osmosis. In other words, it refers to how hard the water would push to get through the barrier in order to diffuse to the other side. Osmotic pressure can be defined as the minimum pressure that must be applied to a solution to halt the flow of solvent molecules through a semipermeable membrane (osmosis). Match. Osmotic Power, also known as Pressure Retarded Osmosis (PRO), is a rapidly growing renewable energy source (RES) that converts the pressure difference between high and low salinity water into hydraulic pressure. Participating colloids displace water molecules, thus creating a relative water molecule deficit with water molecules moving back into the circulatory system within the lower Osmotic Power, also known as Pressure Retarded Osmosis (PRO), is a rapidly growing renewable energy source (RES) that converts the pressure difference between high and low salinity water into hydraulic pressure. It is also defined as the measure of the tendency of a solution to take in a pure solvent by osmosis. Therefore, the osmotic potential is a result of dissolved solutes. Potential osmotic pressure is the maximum osmotic pressure that could develop in a solution if it were separated from its p Medical Definition of osmotic pressure. Osmotic pressure is expressed by the formula: = iMRT (note how it resembles the PV = nRT form of the Ideal Gas Law) where is the osmotic pressure in Osmosis, as defined by Google dictionary, is a process by which molecules of a solvent pass through a semipermeable membrane from a less concentrated solution into a more concentrated one, thus equalizing the concentrations on each side of the membrane. Osmotic pressure formula. Osmotic pressure is a minimum pressure that is supposed to be applied to a solution to halt the incoming flow of its pure solvent across a semipermeable membrane (osmosis). This pressure is caused by differences between the concentrations of dissolved salts within the body and those outside, in the sea.. It is a colligative property and is dependent on the concentration of solute particles in the solution. Symbol . partial pressure the pressure exerted by each of the constituents of a mixture of gases.
This property is dependent upon the concentration of the solute particles present in solution and hence is one of the colligative properties. Osmotic pressure is the same everywhere of the liquid, thus it is calculated considering the whole system. There will be an escape of water and solute into the interstitial space resulting in interstitial edema whenever the hydrostatic In patients with low oncotic pressure, fluid will tend to accumulate in the tissues, resulting in edema. 2. Osmotic pressure is the pressure created by water moving across a membrane due to osmosis. In other words, it refers to how hard the water would push to get through the barrier in order to diffuse to the other side. Osmotic pressure can be defined as the minimum pressure that must be applied to a solution to halt the flow of solvent molecules through a semipermeable membrane (osmosis). Match. Osmotic Power, also known as Pressure Retarded Osmosis (PRO), is a rapidly growing renewable energy source (RES) that converts the pressure difference between high and low salinity water into hydraulic pressure. Participating colloids displace water molecules, thus creating a relative water molecule deficit with water molecules moving back into the circulatory system within the lower Osmotic Power, also known as Pressure Retarded Osmosis (PRO), is a rapidly growing renewable energy source (RES) that converts the pressure difference between high and low salinity water into hydraulic pressure. It is also defined as the measure of the tendency of a solution to take in a pure solvent by osmosis. Therefore, the osmotic potential is a result of dissolved solutes. Potential osmotic pressure is the maximum osmotic pressure that could develop in a solution if it were separated from its p Medical Definition of osmotic pressure. Osmotic pressure is expressed by the formula: = iMRT (note how it resembles the PV = nRT form of the Ideal Gas Law) where is the osmotic pressure in Osmosis, as defined by Google dictionary, is a process by which molecules of a solvent pass through a semipermeable membrane from a less concentrated solution into a more concentrated one, thus equalizing the concentrations on each side of the membrane. Osmotic pressure formula. Osmotic pressure is a minimum pressure that is supposed to be applied to a solution to halt the incoming flow of its pure solvent across a semipermeable membrane (osmosis). This pressure is caused by differences between the concentrations of dissolved salts within the body and those outside, in the sea.. It is a colligative property and is dependent on the concentration of solute particles in the solution. Symbol . partial pressure the pressure exerted by each of the constituents of a mixture of gases. pressure that must be given to a solution to stop the passage of solvent molecules across a semipermeable barrier is known as osmotic pressure (osmosis). Now osmotic pres . Osmotic pressure is a pressure of the solution, which is required in opposite direction, so as to stop the entry of solvent molecules into the cell. TDS increases the osmotic pressure. The term osmose was introduced in 1854 We will look at them one by one. Osmotic pressure is a surface distributed force that is formed in mixtures with solute and solutions present. Osmotic pressure can be defined as the minimum pressure that must be applied to a solution to halt the flow of solvent molecules. Osmotic pressure is the pressure that we need to apply to stop the flow of solvent molecules from a dilute solution to a concentrated solution through a semi-permeable membrane. A third colligative property, osmotic pressure, helped to establish the fundamentals of modern physical chemistry and played a particularly important role in the early days of solution theory. The osmotic pressure is the pressure required to prevent a solution from undergoing osmosis.The basic requirement for this osmotic pressure to occur is the presence of at least two different solutions that are separated from each other by a semi-permeable membrane. The osmotic pressure of a solution is proportional to the molar concentration of the solute particles in the solution. osmotic pressure the pressure required to stop osmosis through a semipermeable membrane between a solution and pure solvent; it is proportional to the osmolality of the solution. The osmotic pressure of blood serum is 7.65 atm at body temperature, 37 C. Osmotic pressure can be defined as the excess pressure which must be applied to a solution to prevent the flow of solvent of low osmotic pressure when they are separated by a perfectly semi-permeable membrane. Osmotic pressure is the basis of filtering ("reverse osmosis"), a process commonly used in water purification. What causes osmotic pressure to develop in a cell? The force in which a solution attracts a solvent (such as water) through a semipermeable membrane. Osmotic pressure is the pressure that stops the process of osmosis. 4.87 Pa C. 0.00487 Pa D. 0.33 Pa Osmotic pressure can also be defined as the pressure applied to a solution in order to nullify osmotic flow.It is a colligative property, which means that solute particles in a solution directly influence the osmotic pressure. So the solute is dissolved in the solvent, and so we have a net migration of the water molecules from this solution that has a low solute concentration to one that has a higher solute concentration. The pressure of the pure solvent is p, while in osmotic equilibrium the solution is subject to an additional pressure , the osmotic pressure, yielding the equilibrium condition.
The osmolarity is often determined We call this osmosis. The least pressure required to apply to a solution in order to stop the flow of solvent molecules across a semipermeable membrane is known as osmotic pressure (osmosis). Osmotic power is the process of converting the pressure differential between water with high salinity and water with lower or no salinity into hydraulic pressure. Osmotic pressure is essentially how water will move in a semipermeable membrane. It is directly proportional to the molar molecules of concentrated solute particles in the given solution. As blood moves through the capillaries, it filters into the tissue space, delivering nutrients to the cells. It is basically a colligative property and is purely dependent on the Created by. It refers to the pressure difference between the solution and pure solvent resulted after adding solutes to one side. Osmotic PressureCritical Care. Encapsulation by nanoemulsions. Osmosis and Osmotic Pressure. CIRCULATION | Circulatory System Design: Roles and Principles. Body Fluid Distribution. Intensive care medicine. Engineering Fundamentals of Biotechnology. Microbes Culture Methods. Role of ionomics in plant abiotic stress tolerance. More items Osmotic pressure and tonicity often are confusing to people. Both are scientific terms pertaining to pressure. Osmotic pressure is the pressure of a solution against a semipermeable membrane to prevent water from flowing inward across the membrane. Tonicity is the measure of this pressure. = iCRT is the formula used for finding the osmotic pressure of a given solution. A third colligative property, osmotic pressure, helped to establish the fundamentals of modern physical chemistry and played a particularly important role in the early days of solution theory. The osmotic pressure brings the material back to the capillary. In above section, we discussed that to find osmotic pressure, we use the value of solute concentration. Test. Osmotic pressure is a colligative property of a solution, meaning the number of particles matter more than the identity of the particles. 10-2 bar. Read Or Download Gallery of how to calculate osmotic pressure in reverse osmosis - Osmoic Pressure Formula Pgh | osmotic pressure formula examples what is osmotic pressure video, how to calculate osmotic pressure of a solution, the osmotic pressure of a solution prepared by, solved the osmotic pressure of an aqueous solution at 300, membrane, from a solution that has a lower concentration of solutes.
From the formula, Osmotic pressure = CRT. Oncotic pressure is a form of pressure in the circulatory system which encourages water to cross the barrier of the capillaries and enter the circulatory system. The water to be purified is placed in a chamber and put under an amount of pressure greater than the osmotic pressure exerted by the water and the solutes dissolved in it. Symbol . partial pressure the pressure exerted Tonicity is the measure of this pressure. Osmotic pressure is a colligative property of a substance since it depends on the concentration of the solute and not its chemical nature. Osmotic Pressure: The hydrostatic pressure exerted by the column of the solution which is just sufficient to prevent the osmosis is called osmotic pressure. It generates a hydrostatic pressure caused by a difference in the concentration of each component when separated by a membrane. osmotic: [adjective] of, relating to, caused by, or having the properties of osmosis. When the minimum amount of pressure is applied to the solution in order to stop the flow of molecules of solvent transferring through a semi-permeable membrane is known as osmotic pressure. Terms in this set (43) Diffusion is the process in which molecules move from an area of (larger/smaller) concentration to an area of (greater/lesser) concentration of that type of molecule. Concept: Colligative Properties and Determination of Molar Mass - Osmosis and Osmotic Pressure. b : the pressure that must be applied to a solution to just prevent osmosis. How many grams of. The deaf pressure that is applied to stop the action of osmosis is called osmotic pressure. Water potential is the measure of the potential energy in the water while the osmotic potential is the part of the water potential that results from the presence of solute particles. a : the maximum pressure that develops in a solution separated from a solvent by a membrane permeable only to the solvent. : the pressure produced by or associated with osmosis and dependent on molar concentration and absolute temperature: as. Osmotic pressure is the difference between blood in the capillaries and interstitial fluid between the cells, according to Kimballs Biology Pages. Second Definition: To prevent osmosis when a solution is separated from the solvent by a semi permeable membrane, at least the external pressure exerted is called the osmotic pressure of that solution. The osmotic pressure can be determined by concentration of solute. 2. This hydraulic pressure can be employed to power a generator that produces electricity. Learn. Osmotic pressure arises from the tendency of a pure solvent to move through a semipermeable membrane and into a solution containing a solute to which the membrane is impermeable. This pressure, which is the difference in pressure across the membrane, is what is referred to as osmotic pressure. Osmotic pressure is greatly influenced by the adhesion (electrostatic forces) between the liquid (water or other) and some solid lattice, like a semi-permeable membrane. Osmotic pressure develops in the cell that originally had the higher concentration of impermanent solute. Now, the above statement has many terms that need a thorough explanation. If the concentration of solutes on both sides of the membrane is equal, then there is no tendency for water to move across the membrane and no osmotic pressure. The oncotic pressure or colloidal osmotic pressure is the osmotic pressure developed due to the presence of colloids in a solution. There's other arguments for osmosis. Osmotic pressure is closely related to some other properties of solutions, the colligative properties. What is osmotic pressure? Osmotic pressure: The excess of pressure on the side of the solution, that stops the net flow of solvent into the solution through a semipermeable membrane is called osmoticpressure. Osmotic pressure is the force caused by a solution passing through a semi permeable surface by osmosis, which is equal to the force required to resist the solution from passing back through the surface. A: Given information: Osmotic pressure = 7.65 atm Temperature = 37 Volume of solution = 1 L. Q: 5. It is a colligative property that is regulated by the concentration of solute particles in the solution. A: The expression of molarity and further number of moles of solute can be substituted in the. This definition An osmotic pressure is a physical quantity dependent only on the solution's concentration (s) and temperature. Be careful: higher solvent concentration implies lower solute concentration.All mass transport properties occur from higher concentration to lower concentration (of the
What is Osmotic Pressure?
The solution of higher osmotic pressure is utilized to push the water through a semi-permeable membrane so that the feed solution (the solution with lower osmotic pressure) ends up becoming concentrated as the higher pressure solution dilutes. Osmotic pressure can be described as the pressure of a water solution of salts exerted in either direction against a semipermeable membrane. It is a colligative feature that is influenced by The osmotic pressure of pure water is always zero and it increases with the increase of solute concentration. The third factor is the permeability of the capillary membranes. Previous question Next question. Osmosis is especially important in medicine and biology, but in recent years it has also been applied industrially to problems such as the concentration of fruit juices, the desalting of Osmotic pressure can be explained as the pressure that is exerted to the solution side to prevent fluid movement when a semi-permeable membrane differentiates a solution from pure water. Osmotic pressure is an important factor that affects cells. Osmosis is the net movement of solvent molecules through a partially permeable membrane into a region of higher solute concentration. The intent of osmosis is to equalize the solute concentrations on the two sides. Osmosis is essential in biological systems because biological membranes