 A semipermeable membrane is tied across the open end of a thistle tube. People have used salt to preserve meat, fish and vegetables since agriculture first began Water bath canning is a faster, lower temperature preserving process that is for high-acid foods Salt is harvested in two main ways: from salt mines and by evaporating sea Thousands of years later, a concentrated form of salt water,
A semipermeable membrane is tied across the open end of a thistle tube. People have used salt to preserve meat, fish and vegetables since agriculture first began Water bath canning is a faster, lower temperature preserving process that is for high-acid foods Salt is harvested in two main ways: from salt mines and by evaporating sea Thousands of years later, a concentrated form of salt water,
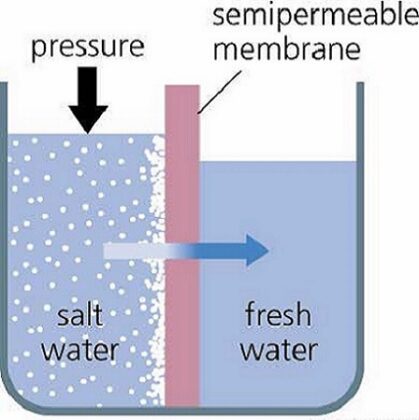
 This inhibits, the reabsorption of water and dissolved substances, and causes an increase in urine flow.. What does osmotic pressure depend on? Search: How Does Salt Preserve Food. Total plasma osmotic pressure = 1 x 0.082 x 310 x 0.001 x 760 x 280 = 5409 mmHg. It would not be an exaggeration to say that fluids are prominently responsible for the genesis and survival of life on earth. Concept: Osmotic Pressure Concept Overview: Osmosis is simply the flow of solvent molecules through a semipermeable membrane from higher solvent concentration to lower solvent concentration. Ask an expert. What does osmotic pressure tell us? Osmotic Pressure Equation is the osmotic pressurei is dimensionless van t Hoff indexc is the molecular concentration of solute in the solutionR is the ideal gas constantT is the temperature in kelvins Osmosis can be defined as the net movement or flow of solvent molecules through a semipermeable membrane driven by osmotic pressure differences across the membrane, to try to equal the concentration of the solute on the two sides of the membrane itself. your sodium acetate dissociates into sodium and acetate, and therefore the n = 2. The tube is then partially filled with a solution of sugar or alcohol in water and immersed in a beaker of water. It is a colligative property that is regulated by the concentration of solute particles in the solution. In fact, osmosis is going on in your body right now as your biological systems work to maintain balance in your blood chemistry.
This inhibits, the reabsorption of water and dissolved substances, and causes an increase in urine flow.. What does osmotic pressure depend on? Search: How Does Salt Preserve Food. Total plasma osmotic pressure = 1 x 0.082 x 310 x 0.001 x 760 x 280 = 5409 mmHg. It would not be an exaggeration to say that fluids are prominently responsible for the genesis and survival of life on earth. Concept: Osmotic Pressure Concept Overview: Osmosis is simply the flow of solvent molecules through a semipermeable membrane from higher solvent concentration to lower solvent concentration. Ask an expert. What does osmotic pressure tell us? Osmotic Pressure Equation is the osmotic pressurei is dimensionless van t Hoff indexc is the molecular concentration of solute in the solutionR is the ideal gas constantT is the temperature in kelvins Osmosis can be defined as the net movement or flow of solvent molecules through a semipermeable membrane driven by osmotic pressure differences across the membrane, to try to equal the concentration of the solute on the two sides of the membrane itself. your sodium acetate dissociates into sodium and acetate, and therefore the n = 2. The tube is then partially filled with a solution of sugar or alcohol in water and immersed in a beaker of water. It is a colligative property that is regulated by the concentration of solute particles in the solution. In fact, osmosis is going on in your body right now as your biological systems work to maintain balance in your blood chemistry.
Suppose that you take a container and divide it into two compartments using a thin membrane that contains microscopic pores; the pores are The osmotic pressure of plasma proteins regulates water to flow from the protein- free intestinal fluid into the blood vessels. For a plasma osmolality of 280 mOsm/kg at 37C, total osmotic pressure is about 5409mmHg (ie about 7.1 atmospheres!) Hydrostatic pressure pushes fluid out of the capillaries and colloid osmotic pressure causes reabsorption. Calculating the osmotic pressure formula chemistry is done using, =iMRT. Osmosis is a common biological process in which water moves from a dilute to a concentrated solution, across a semipermeable membrane, to balance the concentrations. Example: To determine the molar mass of unknown salt, 1g of it is dissolved in a solvent to make 10 ml of solution. Osmotic pressure can be described as the pressure of a water solution of salts exerted in either direction against a semipermeable membrane. The temperature and the initial concentration of the solute affect osmotic pressure. Osmotic pressure is the minimum pressure which needs to be applied to a solution to prevent the inward flow of its pure solvent across a semipermeable membrane. Osmotic pressure is an important factor that affects cells. Osmosis is the net movement of solvent molecules through a partially permeable membrane into a region of higher solute concentration. The intent of osmosis is to equalize the solute concentrations on the two sides. Osmosis is essential in biological systems because biological membranes It was first discovered in plants which use osmosis to Both processes rely on osmosis with membranes.The key waste product is brackish water.This byproduct is the result of natural The osmotic pressure can be defined as the pressure difference found between two solutions at a state of equilibrium, but with different amount of salinity, when the two solutions are kept at the two sides of a semipermeable membrane. An answer explanation states that in a hypotonic medium, there is greater osmotic pressure in the cell than in the medium, which decreases following the movement of water into the cell. ADVERTISEMENTS: Monash University (Australia) You can use modified Van't Hoff equation to calculate the osmotic pressure for binary or tertiary mixture. To set up a reverse osmosis desalinator, you first need an intake pump at the source of the seawater. Two practical methods for this are reverse electrodialysis (RED) andpressure retarded osmosis (PRO). Use of this pressure to generate power was proposed in the 1970s, but a better membrane was needed to make it cost-effective. There will be an escape of water and solute into the interstitial space resulting in interstitial edema whenever the hydrostatic pressure Critical in this process is the stoma. Soluble, non-absorbable PEG 3350 hydrates, softens and eases stools by gently attracting water in the colon through a process known as osmosis. The solvent passes from the dilute to the more concentrated solution through the membrane separating the two solutions. Osmotic pressure is not the only parameter to keep controlled. Two practical methods for this are reverse electrodialysis (RED) andpressure retarded osmosis (PRO). In chemistry texts, it is usually expressed in terms of the molarity of the solution and given the symbol . a. decreases renin secretion. Pressure differentials govern fluid movement across physiologic semi-permeable membranes, and two of these forces are hydrostatic/hydraulic pressure and osmotic pressure. Osmotic diuretics are the least used type of diuretics. Pressure comes from a water column on the salted side of the membrane. The osmotic pressure of a dilute solution is found to obey a relationship of the same form as the ideal gas law: In chemistry texts, it is usually expressed in terms of the molarity of the solution and given the symbol . The osmotic pressure of a solution varies directly with absolute temperature in the same way as the pressure of a gas varies when its volume is kept constant. Osmotic pressure is a colligative substance property because it depends on the concentration of the solute but not its chemical nature. Osmotic pressure is the "sucking" of solvent toward an area of hypertonicity (higher solute concentration). The osmotic pressure of a dilute solution is found to obey a relationship of the same form as the ideal gas law: In chemistry texts, it is usually expressed in terms of the molarity of the solution and given the symbol . To calculate osmotic pressure, use the following formula: The lowest force per unit of area, i.e. This paper is a compelling example of an effect of osmotic pressure on enzyme function. Osmotic pressure depends on the concentration of solute particles. Osmotic pressure is a surface distributed force that is formed in mixtures with solute and solutions present. What variable affects osmotic pressure? T is the absolute temperature (K) V is the volume. The third factor is the permeability of the capillary membranes. d. decreases aldosterone secretion. This pressure is caused by differences between the concentrations of dissolved salts within the body and those outside, in the sea.. Hydrostatic pressure ensures proper supply of blood to all parts of the body, whereas osmotic pressure is responsible for the exchange of all necessary fluids. Hydrostatic pressure pushes fluid out of the capillaries and colloid osmotic pressure causes reabsorption. All else staying equal, this gives a direct proportional relationship between temperature and pressure. We calculate the osmotic pressure, (pi), using the following equation: M is the molar concentration of dissolved species (units of mol/L).
Pressure is defined as the force applied on a unit area perpendicularly. They form all of our environment and the elements in it. The term osmolarity is used to describe the number of solute particles in a volume of fluid. I have learnt that in an electrochemical cell, the osmotic pressure in the solution hinders the flow of ions from the electrode to the solution, rather some ions may accumulate on the electrode because of this osmotic pressure. It is just an expansion of Roult's Law i.e. If the medium is hypotonic relative to the cell cytoplasm, the cell will gain water through osmosis.If the medium is isotonic, there will be no net movement of water across the cell membrane.If the medium is hypertonic relative to the cell cytoplasm, the cell will lose water by osmosis. Two solutions of different solutes, for example alcohol and sugar, will each have the same osmotic pressure, provided they have the same concentration. Step 1: Determining the van t Hoff factor. Hydrostatic pressure or blood pressure is the pressure exerted by blood on the capillary walls. Hydrostatic pressure ensures proper supply of blood to all parts of the body, whereas osmotic pressure is responsible for the exchange of all necessary fluids. Osmotic Power, also known as Pressure Retarded Osmosis (PRO), is a rapidly growing renewable energy source (RES) that converts the pressure difference between high and low salinity water into hydraulic pressure. . Which of the following would result in no change in osmotic pressure? The main substance responsible for the osmotic pressure between blood and tissue fluid are the plasma proteins. Suppose w 2 is the mass of solute having molar mass M 2 in a solution of volume V, then we can write, =w2RT/M2V.
Osmotic pressure is a basic chemical principle, but it also plays a role in biology. The Osmotic Pressure calculation example is given with a brief description below. What effect do you think increasing the Na+ Cl will have? A molecule is osmotically active if it contributes towards osmotic pressure - that is, a molecule is osmotically active if it is causing osmosis to occur. =osmotic pressure. The high osmolality of the osmotic layer causes water to flux into the pump through a semipermeable membrane which forms the outer surface of the pump. Briefly speaking, intracellular fluid of red cells is isotonic with the red cell membrane in 0.92% NaCl solution. Osmotic pressure is the minimum pressure which needs to be applied to a solution to prevent the inward flow of its pure solvent across a semipermeable membrane. ALZET pumps operate because of an osmotic pressure difference between a compartment within the pump, called the osmotic layer, and the tissue environment in which the pump is implanted. Potential osmotic pressure is the maximum osmotic pressure that could develop in a solution if it were separated from its pure solvent by a se It would not be an exaggeration to say that fluids are prominently responsible for the genesis and survival of life on earth. Osmoles are used to describe the concentration in terms of number of particles - a 1 osmolar solution contains 1 mole of osmotically-active particles (molecules and ions) per liter. They work by increasing osmolality (the concentration of osmotically active particles in a solution). It is also defined as the measure of the tendency of a solution to take in a pure solvent by osmosis. 5. Living red cells, if suspended in 0.92% NaCl solution, neither gain nor lose water. P is the osmotic pressure, n is the number of particles into which the substance dissociates, i.e. Good work lactobacillus! Osmotic pressure obtained is employed to calculate molar mass. Osmotic pressure depends on the number of osmotically active, non diffusible particles in the solutions separated by the membrane. b. increases ADH secretion. When a solution and a pure solvent are separated by a semipermeable membrane, How do you find osmotic pressure from atmospheric pressure? water moves from a dilute to a concentrated solution, across a semi-permeable membrane, to balance the concentrations. If the salt ions are captured completely by the membrane, the passing of water through the membrane will create a In this study, we examined the mechanism by which MgSO(4) increases the intestinal AQP3 expression level by using the human colon cancer This is the same as for molecules in the gas phase, and described by the ideal gas law: pV=nRT. Each mOsm/kg of solute contributes about 19.32mmHg to the osmotic pressure. Osmotic pressure is the external pressure needed to prevent the solvent from crossing the membrane. Osmotic pressure refers to tendency for a liquid solution to diffuse therefore moving from a lower to higher concentration across a membrane. Osmosis is a special type of simple diffusion (specifically for water). Solved Examples. Answer (1 of 9): Osmosis is the tendency of a solute to move from An area of higher Concentration to an area of lower Concentration to equalize Concentrations on both sides of a semi permeable membrane. An osmotic pressure is used to measure the ability of water to move from one solution to another solution through osmosis. Read More. by the osmotic pressure formula: = i.M.R.T . Osmotic Pressure. Osmotic Pressure. Osmosis is the movement of solvent molecules through a semipermeable membrane into an area that has a higher solute concentration. R=Universal Gas constant: T=Temperature. 2. An osmotic oral drug delivery system is one which depends on the mechanics of osmotic pressure variations to regulate the delivery of the drug or active agent. Look it up now! Basically, osmotic agents, such as polyethylene glycol found in MiraLAX , work naturally with the water in the colon to unblock a persons system. Osmotic pressure is the pressure developed by diffusion of a liquid or solvent through a membrane. This hydraulic pressure can be employed to power a generator that produces electricity. Why does increasing the pressure increase the filtration rate? Be careful: higher solvent concentration implies lower solute concentration.All mass transport properties occur from higher concentration to lower concentration (of the molecules Osmotic power, salinity gradient power or blue energy is the energy available from the difference in the salt concentration between seawater and river water.Two practical methods for this are reverse electrodialysis (RED) and pressure retarded osmosis (PRO). c. uses the pulling force of albumin. Either freezing point depression or osmotic pressure can be used to calculate the other. How does colloid osmotic pressure work? If a molecule is dissolved in a liquid and it cannot cross a membrane but the liquid can, then it will be osmotically active. converts the pressure differential between water with high salinity and water with lower or no Aims: We have suggested that an osmotic laxative, magnesium sulphate (MgSO(4)), may act as a cathartic in a very rational manner by increasing the aquaporin 3 (AQP3) expression level and by changing osmotic pressure in the colon. d. decreases aldosterone secretion. A solvent and a solute together make a solution. Osmotic pressure can be demonstrated with the apparatus shown in the figure below. Calculate the molar mass of the salt at 20 o C. b. increases ADH secretion. When the peptidoglycan ruptures, osmotic pressure differences between the inside of the bacteria and the outside environment cause the internal components of the bacteria to leak out. Molarity is the number of moles of solute per litre of the solution. Osmotic Pressure.
The osmometer shows that the osmotic pressure of this solution is 1.12 atm. Osmotic power, salinity gradient power or blue energy is the energy available from the difference in the salt concentration between seawater and river water. Interestingly, it does not depend on what is dissolved. protacanthopterygians. Restriction enzymes are normally very selective in the base sequences of sites at which they cut DNA, but in some conditions they show cutting at off-target sites, called "star activity." Best not to look directly at it. c. uses the pulling force of albumin. Osmotic pressure is the pressure caused by water at different concentrations due to the dilution of water by dissolved molecules (solute), notably salts and nutrients. What was the effect of increasing the pressure above the beaker on filtration rate and filtrate concentration explain? Osmotic potential describes potential energy of water that will undertake this phenomenon across a semipermeable membrane. Osmotic pressure is the external pressure needed to prevent the solvent from crossing the membrane. This pressure is often called hydrostatic ('water-stopping') pressure.
pressure that must be given to a solution to stop the passage of solvent molecules across a semipermeable barrier is known as osmotic pressure (osmosis). The least pressure required to apply to a solution in order to stop the flow of solvent molecules across a semipermeable membrane is known as osmotic pressure (osmosis). It generates a hydrostatic pressure caused by a difference in the concentration of each component when separated by a membrane. Next, you need to create flow through the membrane. Osmotic pressure, osmosis, and plasma membranes. Osmotic pressure is driven by the tendency of the solute molecules that are not glueing together to take up as much space as they can get. Osmotic Pressure given density of solution SolutionConvert Input (s) to Base UnitEvaluate FormulaConvert Result to Output's Unit Click to see full answer Considering this, what is osmotic pressure and how does it work? Another common but important application of osmotic pressure is in the desalination and purification of seawater using the process of reverse osmosis. Ask an expert. Osmotic diuretics are mainly administered via intravenous route and are used to treat: Intracranial pressure (increased pressure in the brain) associated with brain mass Intraocular pressure (fluid pressure inside the eye) Anuria/ oliguria (unable to pass urine/passes less urine) A third colligative property, osmotic pressure, helped to establish the fundamentals of modern physical chemistry and played a particularly important role in the early days of solution theory. The measurement of osmotic pressure is useful to determine the molecular weights of compounds. We need to know the molar concentration of dissolved species in order to calculate the osmotic pressure of an aqueous solution. Hydrostatic pressure and osmotic pressure are two classifications of pressure that are in relation with fluids. Effective osmotic pressure definition at Dictionary.com, a free online dictionary with pronunciation, synonyms and translation. It is a colligative feature that is influenced by the solute particle concentration in Osmotic Pressure. Osmotic power, salinity gradient power or blue energy is the energy available from the difference in the salt concentration between seawater and river water. Osmotic pressure is affected by concentration and temperature. C=molarity of the solution. How does colloid osmotic pressure work? They form all of our environment and the elements in it. I thought osmotic pressure opposes the movement of water during osmosis. Q.1: One mole of table salt is dissolved into water of volume of one liter. The Center for Student Success and Academic Counseling CSSAC Osmotic pressure depends on the concentration of solute particles. I have learnt that in an electrochemical cell, the osmotic pressure in the solution hinders the flow of ions from the electrode to the solution, rather some ions may accumulate on the electrode because of this osmotic pressure. It is also defined as the measure of the tendency of a Osmotics reduce osmotic pressure in the blood and blood vessels. a. decreases renin secretion. Guard cells use osmotic pressure to open and close stomata, allowing plants to regulate the amount of water and solutes within them. As with gases, the laws of osmotic pressure hold closely only for dilute solutions. How Osmoregulation Works Osmosis is the movement of solvent molecules through a semipermeable membrane into an area that has a higher solute concentration. This increases the pressure on one side of the membrane. Osmotic pressure, vapor pressure lowering, boiling point elevation, and freezing point depression, are all measures of the same chemical potential of the solvent, which does not have to be water. Osmosis is the diffusion of water across a membrane in response to osmotic pressure caused by an imbalance of molecules on either side of the membrane. Corrosionpedia Explains Osmotic Pressure. One notable exception, however, consists of the osmotic control of electrical activity in SON neurons which, in the rat, contributes to the regulation of natriuresis and diuresis through effects on the secretion of oxytocin and vasopressin. These laws of osmotic pressure have been thoroughly verified by accurate observations. This will cause water to pass through the salted side of the membrane to the unsalted side. A third colligative property, osmotic pressure, helped to establish the fundamentals of modern physical chemistry and played a particularly important role in the early days of solution theory. How does osmotic pressure work? Osmotic pressure can be determined using the equation shown here. What is Osmotic Pressure? R is the universal gas constant, which is 0.082 L atm mol -1 K -1. Stomata (multiple stoma) are located on the outermost cellular layer of leaves, stems, and other plant parts. iii. Osmotic pressure depends on the temperature and the original concentration of solute.