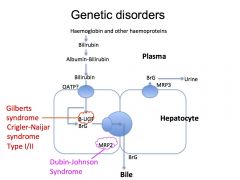
 UDP Glucuronyl transferase Deficiencies - Crigler Najjar, Gilbert Syndrome. A community for healthcare professionals and students to share free online learning resources. openmed.co.in/2022/0 6.
UDP Glucuronyl transferase Deficiencies - Crigler Najjar, Gilbert Syndrome. A community for healthcare professionals and students to share free online learning resources. openmed.co.in/2022/0 6.  Life expectancy is less than a year. There is a absent UDP-glucuronyl transferase (incompatible with living more than a few years) mild UDP-glucuronyl transferase activity ; mild bilirubin uptake ; Autosomal recessive inheritance very common in population; Presentation: Symptoms. (1) Gilbert syndrome is caused by a 25% to 50% reduction in glucuronidation activity of the UGT1A1 enzyme and is characterized by episodes of mild intermittent jaundice and the absence of liver disease. Gilbert syndrome is a hereditary condition which can result in jaundice.. Upozornenie: Prezeranie tchto strnok je uren len pre nvtevnkov nad 18 rokov! effect of phototherapy, new england journal of medicine 282: 375 (1970). Gilbert's syndrome (zh eel-bairz) n. familial unconjugated hyperbilirubinaemia: a condition caused by an inherited congenital deficiency of the enzyme UDP glucuronyl transferase in the liver cells. ).
Life expectancy is less than a year. There is a absent UDP-glucuronyl transferase (incompatible with living more than a few years) mild UDP-glucuronyl transferase activity ; mild bilirubin uptake ; Autosomal recessive inheritance very common in population; Presentation: Symptoms. (1) Gilbert syndrome is caused by a 25% to 50% reduction in glucuronidation activity of the UGT1A1 enzyme and is characterized by episodes of mild intermittent jaundice and the absence of liver disease. Gilbert syndrome is a hereditary condition which can result in jaundice.. Upozornenie: Prezeranie tchto strnok je uren len pre nvtevnkov nad 18 rokov! effect of phototherapy, new england journal of medicine 282: 375 (1970). Gilbert's syndrome (zh eel-bairz) n. familial unconjugated hyperbilirubinaemia: a condition caused by an inherited congenital deficiency of the enzyme UDP glucuronyl transferase in the liver cells. ). Gilbert's syndrome is an autosomalrecessive disease. hide. 2 comments. r/Foamed. absent UDP-glucuronyl transferase (incompatible with living more than a few years) In its typical form, hyperbilirubinemia is first noticed as intermittent mild jaundice in adolescence. largely asymptomatic; occasional reccurent mild jaundice associated with fasting, stress, and EtOH intake Gilbert disease is a hereditary condition caused by a mild form of genetic deficiency of UDP-glucuronyl transferase 1A1 (UGT1A1), an enzyme metabolizing bilirubin through glucuronidation, resulting in impaired bilirubin metabolism and clearanceCharacterized by intermittent, mild, asymptomatic jaundice in the absence of Explore the latest full-text research PDFs, articles, conference papers, preprints and more on UGT. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology Disposition of Lorazepam in Gilbert's Syndrome: Effects of Fasting, Feeding, and Enterohepatic Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1994 / 10 Vol.
 Gilbert syndrome is due to a genetic variant in the UGT1A1 gene which results in decreased activity of the bilirubin uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase enzyme.
Gilbert syndrome is due to a genetic variant in the UGT1A1 gene which results in decreased activity of the bilirubin uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase enzyme.  This is a glucuronidation reaction. openmed.co.in/2022/0 2 comments. Bosma et al. (1995) found that the coding region of the UGT1A1 gene was normal in 10 patients with Gilbert syndrome, but that these patients were homozygous for 2 extra bases (TA) in the TATAA element of the 5-prime promoter region of the gene; they found A (TA)7TAA ( 191740.0011) rather than the normal A (TA)6TAA. This testing is performed on a patient's blood sample. Hepatic bilirubin udp-glucuronyl transferase activity in liver disease and gilbert's syndrome. Abstract Background The most common mutations in Gilbert's syndrome are associated with the promoter region of the gene (rs8175347) and the Hepatic (liver) involvement in some diseases can be of crucial importance. Gilbert's syndrome is an inherited disorder that affects approximately 8 percent of the population, men more than women. A community for healthcare professionals and students to share free online learning resources. 3. Ngoi ra c th do sa m c nhiu beta-caroten, Patients become mildly jaundiced, especially if they fast or have some minor infection. save.
This is a glucuronidation reaction. openmed.co.in/2022/0 2 comments. Bosma et al. (1995) found that the coding region of the UGT1A1 gene was normal in 10 patients with Gilbert syndrome, but that these patients were homozygous for 2 extra bases (TA) in the TATAA element of the 5-prime promoter region of the gene; they found A (TA)7TAA ( 191740.0011) rather than the normal A (TA)6TAA. This testing is performed on a patient's blood sample. Hepatic bilirubin udp-glucuronyl transferase activity in liver disease and gilbert's syndrome. Abstract Background The most common mutations in Gilbert's syndrome are associated with the promoter region of the gene (rs8175347) and the Hepatic (liver) involvement in some diseases can be of crucial importance. Gilbert's syndrome is an inherited disorder that affects approximately 8 percent of the population, men more than women. A community for healthcare professionals and students to share free online learning resources. 3. Ngoi ra c th do sa m c nhiu beta-caroten, Patients become mildly jaundiced, especially if they fast or have some minor infection. save. Hepatic (liver) involvement in some diseases can be of crucial importance. 12.1k members in the Foamed community. Upozornenie: Prezeranie tchto strnok je uren len pre nvtevnkov nad 18 rokov! Abstract A recently described method for assaying the specific hepatic enzyme responsible for the conjugation of bilirubin was applied to specimens of liver obtained at laparotomy or
More severe types of glucuronyl transferase disorders such as CriglerNajjar syndrome (types I and II) are much more severe, with 010% UGT1A1 activity, with sufferers at risk of brain damage in infancy (type I) and teenage years (type II). google scholar. Inheritance tends to follow an autosomal recessive pattern. Questions frquentes. 1969 Jun 5;280(23):1266-71. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196906052802303. Gilbert syndrome is generally considered to be an autosomal recessive disorder, although autosomal dominant inheritance has been suggested in some cases. This syndrome is manifested clinically by coughing induced by seemingly innocuous stimuli such as changes in ambient temperature, laughing, talking on the phone or aerosol exposure.
It also helps to detoxify aspirin, menthol, vanillin (synthetic vanilla), food additives such as benzoates, some hormones and bilirubin. CNS-II is caused by a deficiency of UDP-glucuronyl transferase (UGT), which is encoded by the UDP-glucuronyl transferase 1A1 gene ( UGT1A1 ). gorodischer, r, congenital nonobstructive, nonhemolytic jaundice . Gilberts syndrome is a form of hereditary non-hemolytic jaundice transmitted by autosomal dominant pattern. bilirubine conjugue directe. Pathology. What causes Gilbert's syndrome?
Many people never have symptoms. The reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme bilirubin UDPglucurony Hepatic Bilirubin UDP-Glucuronyl Transferase Activity in Liver Disease and Gilbert's Syndrome | Continue browsing in r/Foamed. [3] 34; Iss. 'In vitro' assay of bilirubin-UDP glucuronyl transferase activity in the liver of patients with Gilbert's syndrome and a variety of hepatic disorders. share. free easter basket svg files for cricut; yorushika hitchcock lirik terjemahan; owner financing homes georgia; used electric mobility scooters for sale near maryland The genetic basis of UDP Glucuronyl transferase Deficiencies - Crigler Najjar, Gilbert Syndrome. Author links open overlay panel
Patients become mildly jaundiced, especially if they fast or have some minor infection. Uridine diphosphate-glucuronyl transferase activity is reduced resulting in indirect hyperbilirubinemia. CriglerNajjar Syndrome type II (CNS-II) is an autosomal recessive hereditary condition of unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia without hemolysis, with bilirubin levels ranging from 102.6 mol/L to 342 mol/L. Gilbert's syndrome. Patients may present with mild jaundice, particularly at times of intercurrent illness. This testing is performed on a patient's blood sample. mildly decreased UDP-glucuronyl transferase OR decreased bilirubin uptake (results in elevated unconjugated bilirubin without overt hemolysis) What causes Crigler-Najjar syndrome, type I? Detailed studies show that patients with Gilbert syndrome have reduced activity of bilirubin glucuronosyltransferase (Bosma et al., 1995, Koiwai et al., 1995). Genetic Heterogeneity of Hyperbilirubinemia Hepatic Bilirubin UDP-glucuronyl Transferase Activity in Patients with Parenchymatous Liver Disease and Gilbert's Syndrome. report. In patients with Gilbert syndrome, uridine diphosphate-glucuronyl transferase activity is reduced to 30% of the normal, resulting in indirect hyperbilirubinemia. A community for healthcare professionals and students to share free online learning resources.
Many of the commonly prescribed drugs are detoxified through this pathway. Occasionally jaundice (a slight yellowish color of the skin or whites of the eyes) may occur.. Gilbert syndrome is due to a genetic variant in the UGT1A1 gene which results in decreased activity of the bilirubin uridine Journal of Clinical Pharmacology Disposition of Lorazepam in Gilbert's Syndrome: Effects of Fasting, Feeding, and Enterohepatic Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1994 / 8 Interesting Facts of Gilbert Syndrome. Find methods information, sources, references or conduct a literature review on UGT openmed.co.in/2022/0 6. Gilbert's syndrome is a common genetic disorder caused by a deficiency of the enzyme UDP-glucuronyl transferase, which leads to an increase in the levels of unconjugated bilirubin. Inheritance tends to follow an autosomal recessive pattern. Gilbert's syndrome Gilbert's syndrome is a common genetic disorder caused by a deficiency of the enzyme UDP-glucuronyl transferase, which leads to an increase in the levels of unconjugated bilirubin. Gilbert's syndrome is the most common cause of hereditary hyperbilirubinemia [2]. PDF | Background The most common mutations in Gilbert's syndrome are associated with the promoter region of the gene (rs8175347) and the codon region in | Continue browsing in r/Foamed. Recherche d'information mdicale black, m, hepatic bilirubin udp-glucuronyl transferase activity in liver disease and gilberts syndrome, new england journal of medicine 280: 1266 (1969). Slovnk pojmov zameran na vedu a jej popularizciu na Slovensku. N Engl J Med 1969; 280:1266. [ N. A. Gilbert (18581927), French physician] Hepatic bilirubin udp-glucuronyl transferase activity in liver disease and gilbert's syndrome. Hepatic bilirubin udp-glucuronyl transferase activity in liver disease and gilbert's syndrome N Engl J Med . hide. Gilbert syndrome is due to a genetic variant in the UGT1A1 gene which results in decreased activity of the bilirubin uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase enzyme. 2 comments. Gilbert syndrome (GS) is a syndrome in which the liver of affected individuals processes bilirubin more slowly than the majority. [3] UDP Glucuronyl transferase Deficiencies - Crigler Najjar, Gilbert Syndrome. The mutation of uridine diphosphate glucuronyl transferase is seen in 10-16% of the population. glucuronic acid or other type of conjugated metabolite in vivo through enzymatic reaction with an enzyme system such as UDP-glucuronyl transferase. share. familial unconjugated hyperbilirubinaemia: a condition due to an inherited congenital deficiency of the enzyme UDP glucuronyl transferase in the liver cells. [1] [3] It is typically inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern and occasionally in an autosomal dominant pattern depending on the type of variant. Talk to our Chatbot to narrow down your search. What causes Gilbert's syndrome? An assay of bilirubin udp-glucuronyl transferase on needle-biopsies applied to gilbert's syndrome. This disorder develops if you have a mutation in an enzyme called glucuronyl transferase, also known as UDP-glucuronosyltransferase. Occasionally jaundice (a slight yellowish color of the skin or whites of the eyes) may occur.. Gilbert syndrome is due to a genetic variant in the UGT1A1 gene which results in decreased activity of the bilirubin uridine About Community. UNLABELLED: Gilbert syndrome is a common autosomal dominant hereditary condition with incomplete penetrance and characterized by intermittent unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia in the absence of hepatocellular disease or hemolysis. Uridine 5'-diphospho-glucuronosyltransferase (UDP-glucuronosyltransferase, UGT) is a microsomal glycosyltransferase (EC 2.4.1.17) that catalyzes the transfer of the glucuronic acid component of UDP-glucuronic acid to a small hydrophobic molecule. Black and Billing (1969) found hepatic bilirubin UDP-transferase to be about 25% of normal in 11 patients with Gilbert syndrome. The reduced activity of UGT1A1 (UDP-Glucuronyl transferase1A1 enzyme) causes non-conjugated hyperbilirubinemia, and consequently leads to Gilbert's and Crigler-Najjar syndromes ( Maruo et al., 2016; Sugatani et al., 2008 ). 10 Of the many causes of jaundice, Gilbert s syndrome (GS) is probably the most common and most innocu- 12 Black M, Billing BH. Glucuronation, the combining of glucuronic acid with toxins, requires the enzyme UDP-glucuronyl transferase (UDPGT). Gamma-aminobutyric acid GB-Virus Glutamate dehydrogenase Galactose elimination capacity Glomerular filtration rate Gamma-glutamyl transpeptitase Growth hormone-releasing factor Granulocyte macrophage colonic stimul. Gilbert's syndrome. Effect of gilbert's syndrome associated polymorphic alleles (rs8175347 and rs4148323) of UDP-glucuronyl transferase on serum bilirubin level Abstract . The mechanism of jaundice is due to reduced activity of the enzyme UDP-glucuronyl transferase which leads to impaired conjugation and excretion of It is important for the anesthesiologists to understand the pathophysiology of the Many people never have symptoms. A. Gilbert's syndrome (GS) B. Rotor syndrome (RS) C. Crigler-Najjar syndrome (CN) D. Dubin-Johnson (DJ) C. CN is a rare condition that occurs in two forms. N Engl J Med 1969; 280 : 126671 13 Bosma PJ, Chowdhury JR, Bakker C, et al. r/Foamed. Hepatic bilirubin UDP-glucuronyl transferase activity in liver disease and Gilberts syndrome. ENT/H&N/OMF. mildly decreased UDP-glucuronyl transferase OR decreased bilirubin uptake (results in elevated unconjugated bilirubin without overt hemolysis) What causes Crigler-Najjar syndrome, type I? Jaundice in Gilberts syndrome is often triggered by periods of inter-current illness, caloric deprivation, or other physiological stress such as heavy physical exertion, lack of sleep or dehydration. About Community. Gilbert syndrome (GS) is a syndrome in which the liver of affected individuals processes bilirubin more slowly than the majority. Bilirubin pigments were studied in the bile of 20 normal adults, 25 patients with Gilbert's syndrome, 9 children with Crigler-Najjar disease, and 6 patients with hemolysis, to determine how a deficiency of hepatic bilirubin UDP-glucuronosyltransferase would affect the end products of bilirubin biotransformation. Occasionally they have mild abdominal discomfort. report. Posted by 3 days ago. T1 is inherited as an autosomal recessive trait and causes a total deficiency of UDP-glucuronyl transferase. Check the full list of possible causes and conditions now! Auclair C, Hakim J, Boivin P, et al. Bilirubin and paranitrophenol glucuronyl transferase activities of the liver in patients with Gilbert's syndrome An attempt at a biochemical breakdown of the Gilbert's syndrome. dubin & Hepatic UDP-Glucuronyl Transferase Activity Decreased Symptom Checker: Possible causes include Gilbert Syndrome. [1] [3] It is typically inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern and occasionally in an autosomal dominant pattern depending on the type of variant. UDP-glucuronyl transferase; (c) tng ti hp thu bilirubin rut, bi beta-glucuronidase trong phn ca tr s sinh thy phn bilirubin lin hp thnh bilirubin khng lin hp ti hp thu th ng. Diagnosis Schmid (1995) pointed out that Gilbert syndrome is an entirely benign and clinically inconsequential entity, requiring neither treatment nor long-term medical attention. The hatched area indicates the normal range (mean 2 SD. Since there is low glucuronyl transferase activity in the liver there is a risk for anesthetic toxicity with a possibility of a catastrophic outcome. The decreased activity of UDP-glucuronyl transferase makes these patients vulnerable to usual doses of anaesthetic drugs. Avoiding prolonged fasting, maintainence of adequate hydration, use of short acting drugs which undergo least hepatic uptake