 227 Issue 1 p79.e1.
227 Issue 1 p79.e1.  The cell membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of cells and organelles while protecting the cell from its surrounding. Depending on the membrane and the solute, Red blood cell (RBC) is the most abundant cell component with the longest circulation time in the blood [].The annual clinical blood transfusion volume is up to 50 million units approximately, which makes RBC widely available [].Moreover, the RBC membrane is readily extracted and purified since mature RBC lacks nuclei and organelles, facilitating it as a coating
The cell membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of cells and organelles while protecting the cell from its surrounding. Depending on the membrane and the solute, Red blood cell (RBC) is the most abundant cell component with the longest circulation time in the blood [].The annual clinical blood transfusion volume is up to 50 million units approximately, which makes RBC widely available [].Moreover, the RBC membrane is readily extracted and purified since mature RBC lacks nuclei and organelles, facilitating it as a coating 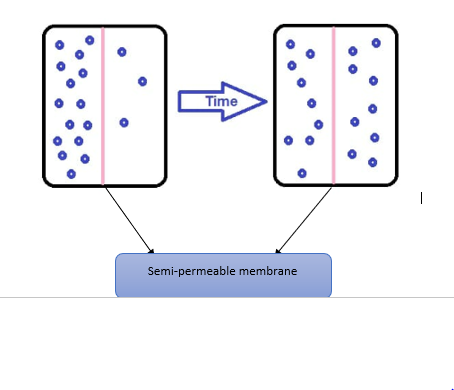 The cell membrane is a multifaceted membrane that envelopes a cell's cytoplasm. Aquapores. (CO2) and oxygen (O2), can move across the plasma membrane by diffusion, which is a passive transport process. The cell membrane is a thin three-layer membrane (8). Chapter 4: Membrane Structure and Function Cell Membrane Proteins: 1) Transport Proteins: Regulate movement of hydrophilic molecules through membrane A) Channel Proteins (e.g. Structure of cell membrane.
The cell membrane is a multifaceted membrane that envelopes a cell's cytoplasm. Aquapores. (CO2) and oxygen (O2), can move across the plasma membrane by diffusion, which is a passive transport process. The cell membrane is a thin three-layer membrane (8). Chapter 4: Membrane Structure and Function Cell Membrane Proteins: 1) Transport Proteins: Regulate movement of hydrophilic molecules through membrane A) Channel Proteins (e.g. Structure of cell membrane. Reference. Passive diffusion and osmosis: Some uncharged molecules, such as carbon dioxide (CO 2) and oxygen (O 2), can move across the cell membrane by diffusion, which is a passive transport process. A familiar example is the perfume of a flower that quickly permeates the still air of a room. The plasma membrane is an important part of a cell, as it provides it with protection and also helps in maintaining a proper shape. Secondary active transport in the nephron. Comparative rates of diffusion through different media.
Singer and Garth Nicolson developed the fluid mosaic model to describe biological membranes. The plasma membrane, which is also called the cell membrane, has many functions, but the most basic one is to define the borders of the cell and keep the cell functional. Cholesterol and various proteins are also embedded within the membrane giving the membrane a variety of functions described below. The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer, made up of two layers of Diffusion of Liquid in Liquid 3. Diffusion is the passive movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. The cell membrane's four primary functions include cell signaling, selective transport, excretion of wastes, and structural support. Dar et al. For example, the diffusion of a molecule across a cell membrane 8 nm thick is 1-D diffusion because of the spherical symmetry; However, the diffusion of a molecule from the membrane to the center of a eukaryotic cell is a 3-D diffusion. Diffusion is a passive process, but active transport requires metabolic energy or an electrochemical gradient for the transportation of molecules across the membrane. Tonicity is a measure of the effective osmotic pressure gradient; the water potential of two solutions separated by a partially permeable cell membrane. 227 Issue 1 p79.e1. Then, by observing cubes of different sizes, you can discover why larger cells might need extra help to transport materials. Modeling Transcription. Quiz 2. ADVERTISEMENTS: The following points highlight the top five experiments on diffusion. Tonicity is a measure of the effective osmotic pressure gradient; the water potential of two solutions separated by a partially permeable cell membrane. Cell biology deals with the study of the structure and functions of cells. Comparative Rates of Diffusion of Different Solutes 5. by Jo Chikwe, MD, FRCS. The fundamental building blocks of all cell membranes are phospholipids, which are amphipathic molecules, consisting of two hydrophobic fatty acid chains linked to a phosphate-containing hydrophilic head group (see Figure 2.7).Because their fatty acid tails are poorly soluble in water, phospholipids spontaneously form bilayers in aqueous solutions, with Diffusion of Solid in Liquid 2. Comparative Rates of Diffusion of Different Solutes 5. Discover the role of diffusion in supplying cells with nutrients and removing wastes. It forms a protective barrier over the body's surface, responsible for keeping water in the body and preventing pathogens from entering, and is a stratified squamous epithelium, composed of proliferating basal and differentiated suprabasal keratinocytes.. Keratinocytes are the major cells, constituting 95% of Passive transport and active transport across a cell membrane article. Comparative rates of diffusion through different media.
Osmosis 3. Active transport is the energy-demanding transfer of a substance across a cell membrane against its concentration gradient, i.e., from lower concentration to higher concentration. The plasma membrane is also referred to as the cell membrane. All biological cells require the transport of materials across the plasma membrane into and out of the cell. The molecules should be small and non-polar to traverse the membrane. Amino acids and nucleic acids are polar and too large to cross the cell membrane. But, other diffusion methods, as well as active transport specifically, occur via transmembrane proteins. Plasma Membrane Proteins. It is commonly used when describing the Materials move within the cells cytosol by diffusion, and certain materials move through the plasma membrane by diffusion (Figure 8.8). DNA to Protein. Heat conduction in fluids involves thermal energy transported, or diffused, from higher to lower temperature. Discover the role of diffusion in supplying cells with nutrients and removing wastes. How do things move across a cell membrane? It is concerned with the life processes, signalling pathways, physiological properties, metabolic properties, chemical properties, A plant membrane is made up of two phospholipid layers called lipid bilayers. The plasma membrane is also referred to as the cell membrane. Welcome to the Whitman College Biology Department's Virtual Pig Dissection (VPD)! The substance can move either in or out of the cells. It protects the integrity of the cell along with supporting the cell and helping to maintain the cell's shape. In our custom-designed flow cell (), a catalyst ink, consisting of carbon powdersupported CoPc and Nafion, was spray coated on hydrophobic carbon paper (that measured 2 cm by 2 cm) with a densely packed layer of microporous carbon to form the gas diffusion electrode (GDE) ().The serpentine cathode and anode flow plates that manipulate
Passive transport and active transport across a cell membrane article. Marinescu et al. When diffusion occurs across a cell membrane, this is considered a type of passive transport, and it requires no energy. All biological cells require the transport of materials across the plasma membrane into and out of the cell. Aquapores. Keep in mind that the cell membrane is a phospholipid bilayer and that both the inside and outside of the cell are water-based. It is often described as the plasma membrane. It forms a protective barrier over the body's surface, responsible for keeping water in the body and preventing pathogens from entering, and is a stratified squamous epithelium, composed of proliferating basal and differentiated suprabasal keratinocytes.. Keratinocytes are the major cells, constituting 95% of Sodium-potassium pump. Diffusion of Solid in Liquid 2. The membrane helps in the entering of solid food into the plant cell in the process of phagocytosis (1) & . glucose transporter) 2) Receptor Proteins: Trigger cell activity when molecule from outside environment binds to protein The movement of a substance across the cell membrane is known as cell transports. The cell membrane is selectively permeable and able to regulate what enters and exits the cell, thus facilitating the transport of materials needed for survival. In our custom-designed flow cell (), a catalyst ink, consisting of carbon powdersupported CoPc and Nafion, was spray coated on hydrophobic carbon paper (that measured 2 cm by 2 cm) with a densely packed layer of microporous carbon to form the gas diffusion electrode (GDE) ().The serpentine cathode and anode flow plates that manipulate Membrane Lipids. Cell biology deals with the study of the structure and functions of cells. Simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and osmosis. diffusion, process resulting from random motion of molecules by which there is a net flow of matter from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration. Diffusion is the net movement of anything (for example, atoms, ions, molecules, energy) generally from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Cell membrane acts as a barrier to most, but not all molecules. Cholesterol can fit into spaces between phospholipids and inhibit the diffusion of water-soluble molecules across the membrane. The cell membrane is an extremely pliable structure composed primarily of two layers of phospholipids (a bilayer). Active Transport 4. Modeling Translation. Dar et al.
glucose transporter) 2) Receptor Proteins: Trigger cell activity when molecule from outside environment binds to protein Diffusion and osmosis.
Plays a major role in the diffusion and osmosis of the plant cells. The plasma membrane, which is also called the cell membrane, has many functions, but the most basic one is to define the borders of the cell and keep the cell functional. Diffusion. Diffusion expends no energy. Level up on the above skills and collect up to 240 Mastery points Start quiz. For a cylindrical cactus, the diffusion from photosynthetic cells on its surface to its It is concerned with the life processes, signalling pathways, physiological properties, metabolic properties, chemical properties, This site is designed as a supplement to laboratory dissections exploring introductory mammalian anatomy and physiology it is basic and many details have been omitted for clarity. DNA to Protein. Glomerular filtration in the nephron. Vesicular Transport. Diffusion Across Semipermeable Membranes. Tonicity depends on the relative concentration of selective membrane impermeable solutes across a cell membrane which determine the direction and extent of osmotic flux. Semipermeable membrane is a type of biological or synthetic, polymeric membrane that will allow certain molecules or ions to pass through it by osmosis.The rate of passage depends on the pressure, concentration, and temperature of the molecules or solutes on either side, as well as the permeability of the membrane to each solute. Amino acids and nucleic acids are polar and too large to cross the cell membrane. by Jo Chikwe, MD, FRCS. The cell membrane is described to be a fluid mosaic. It is commonly used when describing the
The transport across cell membrane is classified into three types. DNA: The Double Helix. Mid-trimester uterine electromyography in patients with a short cervix. Red blood cell (RBC) is the most abundant cell component with the longest circulation time in the blood [].The annual clinical blood transfusion volume is up to 50 million units approximately, which makes RBC widely available [].Moreover, the RBC membrane is readily extracted and purified since mature RBC lacks nuclei and organelles, facilitating it as a coating Plasma Membrane Proteins. This is the currently selected item. (CO2) and oxygen (O2), can move across the plasma membrane by diffusion, which is a passive transport process. Cell-free DNA screening for prenatal detection of 22q11.2 deletion syndrome. Electrically charged, large polar molecules are unable to pass freely through a cell membrane. Sometimes the solution moves to through the phospholipid bilayer or else, its substance is combined with protein to pass through the cell membrane.