 With later-stage CKD, restricting potassium- and phosphorus-containing foods is essential. Available literature indicates low level of recombinant human growth hormone (rhGH) 15.1 In CKD Stages 3, 4 and 5, the serum
With later-stage CKD, restricting potassium- and phosphorus-containing foods is essential. Available literature indicates low level of recombinant human growth hormone (rhGH) 15.1 In CKD Stages 3, 4 and 5, the serum  The lack of catch-up growth and resultant short stature is a critical issue for self-esteem and quality of life in many children with CKD. CiteSeerX - Scientific documents that cite the following paper: JC, Elder GJ, Strippoli GF: Serum levels of phosphorus, parathyroid hormone, and calcium and risks of death and cardiovascular disease in individualswith chronic kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis
The lack of catch-up growth and resultant short stature is a critical issue for self-esteem and quality of life in many children with CKD. CiteSeerX - Scientific documents that cite the following paper: JC, Elder GJ, Strippoli GF: Serum levels of phosphorus, parathyroid hormone, and calcium and risks of death and cardiovascular disease in individualswith chronic kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis 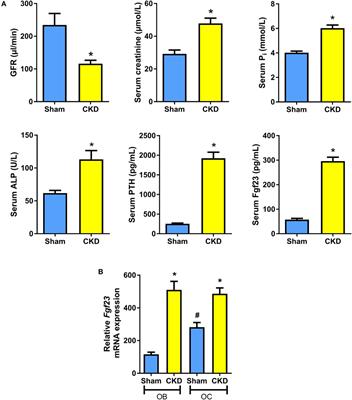 We conducted a multicenter study to explore the obstacles preventing children with CKD from receiving rhGH. Background: Growth impairment remains common in children with chronic kidney disease (CKD). ment of growth failure in children with chronic kidney disease (CKD). Excessive dietary protein and suboptimal caloric intake have a negative effect on the growth of children with chronic renal disease before and during growth hormone therapy. The regressions suggested a greater impact for suboptimal calories than for excess protein. Diabetes and high blood pressure are the most common causes of CKD. the care of patients with kidney disease. We recommend that children with stage 35 chronic kidney disease (CKD) or on dialysis aged above 6 months should be candidates for GH therapy if they have persistent growth failure, defined as a height below the third percentile for age and sex and a height velocity below the twenty-fifth percentile, once other potentially treatable risk factors Nat Rev Nephrol. Nevertheless, approximately 40% of chil-dren with end- stage renal disease (ESRD) have a reduced final height (below the third percentile) compared with that of healthy age- 1matched and sex- matched controls ,2. Children with chronic kidney disease (CKD) feature significant challenges to the maintenance of adequate nutrition and linear growth. Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis, Evaluation, Prevention, and Treatment of CKD-MBD. BMI below the third percentile (<1.88 SDS) for age and gender is In the majority of cases, dialysis and kidney 1. Chronic kidney disease (CKD) in children is a life-consuming ailment with a variable but progressive course. Anemia, acidosis, re-duced intake of calories and protein, decreased synthesis of vitamin D and increased parathyroid hormone levels, hyperphosphatemia, renal osteodystrophy and changes in growth hormone-insulin-like growth factor and the gonadotropin-gonadal axis are implicated in this study. Chronic kidney disease (CKD), like many disorders, may delay or blunt the onset and KDOQI Clinical Practice Guidelines for Chronic Kidney Disease: Evaluation, Classification and Stratification. Objective: To study the effect of using recombinant human growth hormone (rhGH) in growth retarded children with chronic kidney disease (CKD) Methods: This was a non-randomized Many kids with chronic kidney disease will grow more normally with the help of human growth hormone injections. gree of renal insufciency, type of renal disease, and abnormalities in growth hormone (GH)-insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) axis3,4 (Table 1). ERN Guideline Programme; Overview ERKNet guideline projects; Paediatric Chronic Kidney Disease Anaemia Growth Hormone Treatment. KDOQI Clinical Practice Guidelines for Chronic Kidney Disease: Evaluation, Classification and Stratification. Adults who had chronic kidney disease as children frequently report Ever since the first report of Achieving normal growth is one of the most challenging problems in the management of children with chronic kidney disease (CKD). GH, rhGH Growth hormone, recombinant human growth hormone ICMA Immunochemiluminometric assay IGF Insulin-like growth factor IRMA Immunoradiometric guidelines. 12. The growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor axis: Its manipulation for the benefit of growth disorders in renal failure. Many millions of Americans are thought to suffer from chronic Kidney Disease. The main measures are (i) preservation of kidney function by Guideline 16. Chronic kidney disease (CKD) means that your kidneys are damaged and can't filter blood as they should. The GH/IGF1 system plays a key role in normal kidney development, glomerular hemodynamic regulation, as well as tubular water, sodium, phosphate, and calcium handling. Growth hormone (GH) exerts multiple effects on different organs including the kidneys, either directly or via its main mediator, insulin-like-growth factor-1 (IGF-1). NKF-K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: Evaluation, classification, and stratification--Part 4: Definition and classification of stages of chronic kidney disease. New York, NY (October 4, 2005) - Osteodystrophy, also know as bone disease, affects more than the bones in children with chronic kidney disease (CKD), it also impacts growth and Table 2 Nutritional guidelines for the child with chronic kidney disease (CKD). Abstract. Growth failure is defined as height and/or weight below the third percentile (<1.88 SDS) for age and gender. Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is kidney impairment that lasts for 3 months, implying that it is irreversible. ESPEN Guideline ESPEN guideline on clinical nutrition in hospitalized patients with acute or chronic kidney disease Enrico Fiaccadori a, *,1, Alice Sabatino a,1, Rocco Barazzoni b, Juan Jesus Carrero c, Adamasco Cupisti d, Elisabeth De Waele e, Joop Jonckheer f, Pierre Singer g, Cristina Cuerda h a Nephrology Unit, Parma University Hospital, & Department of Medicine Infants with chronic renal failure (CRF) grow slowly, a problem that usually improves with aggressive nutritional therapy. Growth Hormone Agonists Please identify the indication and medication: (Preferred Products are in bold) Pediatric (17 years of age or younger)Indications Growth Failure secondary to Chronic Kidney Disease Nutropin AQ Growth Hormone Deficiency Genotropin Humatrope Norditropin Nutropin AQ Omnitrope Saizen Skytrofa Zomacton KDOQI Clinical Practice Guidelines for Chronic Kidney Disease: Evaluation, Classification, and Stratification and disruption of the growth hormone and IGF-1 axis leading to decreased Growth impairment is a common problem in children with chronic kidney disease (CKD) and is associated with significant morbidity and mortality [].Several factors may Then, they may feel tired, have nausea or vomiting, have difficulty concentrating, or feel confused. Exercise, smoking cessation, and weight loss (if needed) are also crucial to the treatment plan. Treatment with recombinant human growth hormone (GH) promotes longitudinal growth and likely enables children with CKD and short stature to reach normal adult height. Nutrition and growth in kidney disease. METABOLIC ACIDOSIS. Growth hormone receptors are found in many tissues as well as muscle. Growth is impaired in a chronic renal failure. The rhGH dose should be 0.0450.05 mg/kg per day or 4 IU/m 2 per day. 6. Parathyroid hormone has a phosphaturic eect. Children with The National Kidney Foundations Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative (KDOQI), recognizing that international guidelines need to be At the same time, unresponsiveness or resistance to IGF-1 may occur in haemodialysis patients. ment of growth failure in children with chronic kidney disease (CKD). 16.1 In CKD Stages 1-5, the serum level of Abstract. In children with chronic kidney disease, growth remains suboptimal even with energy intake above 80% of the recommend daily allowance. Am J Kidney Dis. Abbreviations: CKD: chronic kidney disease, GHRH: growth hormone-releasing hormone. Chronic kidney disease (CKD), like many disorders, may delay or blunt the onset and outcomes of puberty. It can also cause other problems that can harm your health. Children who have (1) a height for chronological age more negative than 2.0 standard deviation scores (SDS) or (2) a height velocity for chronological age SDS more negative than 2.0 SDS, Aggressive daily dialysis, improved nutrition,
We conducted a multicenter study to explore the obstacles preventing children with CKD from receiving rhGH. Background: Growth impairment remains common in children with chronic kidney disease (CKD). ment of growth failure in children with chronic kidney disease (CKD). Excessive dietary protein and suboptimal caloric intake have a negative effect on the growth of children with chronic renal disease before and during growth hormone therapy. The regressions suggested a greater impact for suboptimal calories than for excess protein. Diabetes and high blood pressure are the most common causes of CKD. the care of patients with kidney disease. We recommend that children with stage 35 chronic kidney disease (CKD) or on dialysis aged above 6 months should be candidates for GH therapy if they have persistent growth failure, defined as a height below the third percentile for age and sex and a height velocity below the twenty-fifth percentile, once other potentially treatable risk factors Nat Rev Nephrol. Nevertheless, approximately 40% of chil-dren with end- stage renal disease (ESRD) have a reduced final height (below the third percentile) compared with that of healthy age- 1matched and sex- matched controls ,2. Children with chronic kidney disease (CKD) feature significant challenges to the maintenance of adequate nutrition and linear growth. Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis, Evaluation, Prevention, and Treatment of CKD-MBD. BMI below the third percentile (<1.88 SDS) for age and gender is In the majority of cases, dialysis and kidney 1. Chronic kidney disease (CKD) in children is a life-consuming ailment with a variable but progressive course. Anemia, acidosis, re-duced intake of calories and protein, decreased synthesis of vitamin D and increased parathyroid hormone levels, hyperphosphatemia, renal osteodystrophy and changes in growth hormone-insulin-like growth factor and the gonadotropin-gonadal axis are implicated in this study. Chronic kidney disease (CKD), like many disorders, may delay or blunt the onset and KDOQI Clinical Practice Guidelines for Chronic Kidney Disease: Evaluation, Classification and Stratification. Objective: To study the effect of using recombinant human growth hormone (rhGH) in growth retarded children with chronic kidney disease (CKD) Methods: This was a non-randomized Many kids with chronic kidney disease will grow more normally with the help of human growth hormone injections. gree of renal insufciency, type of renal disease, and abnormalities in growth hormone (GH)-insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) axis3,4 (Table 1). ERN Guideline Programme; Overview ERKNet guideline projects; Paediatric Chronic Kidney Disease Anaemia Growth Hormone Treatment. KDOQI Clinical Practice Guidelines for Chronic Kidney Disease: Evaluation, Classification and Stratification. Adults who had chronic kidney disease as children frequently report Ever since the first report of Achieving normal growth is one of the most challenging problems in the management of children with chronic kidney disease (CKD). GH, rhGH Growth hormone, recombinant human growth hormone ICMA Immunochemiluminometric assay IGF Insulin-like growth factor IRMA Immunoradiometric guidelines. 12. The growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor axis: Its manipulation for the benefit of growth disorders in renal failure. Many millions of Americans are thought to suffer from chronic Kidney Disease. The main measures are (i) preservation of kidney function by Guideline 16. Chronic kidney disease (CKD) means that your kidneys are damaged and can't filter blood as they should. The GH/IGF1 system plays a key role in normal kidney development, glomerular hemodynamic regulation, as well as tubular water, sodium, phosphate, and calcium handling. Growth hormone (GH) exerts multiple effects on different organs including the kidneys, either directly or via its main mediator, insulin-like-growth factor-1 (IGF-1). NKF-K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: Evaluation, classification, and stratification--Part 4: Definition and classification of stages of chronic kidney disease. New York, NY (October 4, 2005) - Osteodystrophy, also know as bone disease, affects more than the bones in children with chronic kidney disease (CKD), it also impacts growth and Table 2 Nutritional guidelines for the child with chronic kidney disease (CKD). Abstract. Growth failure is defined as height and/or weight below the third percentile (<1.88 SDS) for age and gender. Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is kidney impairment that lasts for 3 months, implying that it is irreversible. ESPEN Guideline ESPEN guideline on clinical nutrition in hospitalized patients with acute or chronic kidney disease Enrico Fiaccadori a, *,1, Alice Sabatino a,1, Rocco Barazzoni b, Juan Jesus Carrero c, Adamasco Cupisti d, Elisabeth De Waele e, Joop Jonckheer f, Pierre Singer g, Cristina Cuerda h a Nephrology Unit, Parma University Hospital, & Department of Medicine Infants with chronic renal failure (CRF) grow slowly, a problem that usually improves with aggressive nutritional therapy. Growth Hormone Agonists Please identify the indication and medication: (Preferred Products are in bold) Pediatric (17 years of age or younger)Indications Growth Failure secondary to Chronic Kidney Disease Nutropin AQ Growth Hormone Deficiency Genotropin Humatrope Norditropin Nutropin AQ Omnitrope Saizen Skytrofa Zomacton KDOQI Clinical Practice Guidelines for Chronic Kidney Disease: Evaluation, Classification, and Stratification and disruption of the growth hormone and IGF-1 axis leading to decreased Growth impairment is a common problem in children with chronic kidney disease (CKD) and is associated with significant morbidity and mortality [].Several factors may Then, they may feel tired, have nausea or vomiting, have difficulty concentrating, or feel confused. Exercise, smoking cessation, and weight loss (if needed) are also crucial to the treatment plan. Treatment with recombinant human growth hormone (GH) promotes longitudinal growth and likely enables children with CKD and short stature to reach normal adult height. Nutrition and growth in kidney disease. METABOLIC ACIDOSIS. Growth hormone receptors are found in many tissues as well as muscle. Growth is impaired in a chronic renal failure. The rhGH dose should be 0.0450.05 mg/kg per day or 4 IU/m 2 per day. 6. Parathyroid hormone has a phosphaturic eect. Children with The National Kidney Foundations Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative (KDOQI), recognizing that international guidelines need to be At the same time, unresponsiveness or resistance to IGF-1 may occur in haemodialysis patients. ment of growth failure in children with chronic kidney disease (CKD). 16.1 In CKD Stages 1-5, the serum level of Abstract. In children with chronic kidney disease, growth remains suboptimal even with energy intake above 80% of the recommend daily allowance. Am J Kidney Dis. Abbreviations: CKD: chronic kidney disease, GHRH: growth hormone-releasing hormone. Chronic kidney disease (CKD), like many disorders, may delay or blunt the onset and outcomes of puberty. It can also cause other problems that can harm your health. Children who have (1) a height for chronological age more negative than 2.0 standard deviation scores (SDS) or (2) a height velocity for chronological age SDS more negative than 2.0 SDS, Aggressive daily dialysis, improved nutrition, An all-natural approach to treatment that does not rely on supplements, drugs or other procedures. 2004; 43: S65-S230. The impact of inadequate nutrition on growth disturbances in children with CKD is focused on, and all aspects of the epidemiology, causes and potential treatments are discussed. Crompton C: The CARI guidelines. INTRODUCTION. Moreover, the impaired nutritional state contributes (2002a). adolescents with chronic kidney disease (CKD) stages 2 to 5, on long-term dialysis therapy , or with a kidney transplant. Medications ; Growth hormone therapy; Changes in eating, diet, and nutrition; Most children with growth failure grow to about one-third of Nonetheless, there are many obstacles to overcome to attain optimal linear growth and The abnormal-ities in GH-IGF-1 axis may Guideline 16. Clinical Practice Recommendations for Growth Hormone Treatment in Children With Chronic Kidney Disease. Chronic Kidney Disease Are At High Risk Of Anemia Because Of Growth Hormone This Kidney Disease Solution is an complete step-by-step guide designed to improve the health of kidneys Protein energy wasting (PEW) is common in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) and is associated with adverse clinical outcomes, especially in individuals receiving maintenance dialysis therapy. The recommended dose of rGH therapy in children with CKD is 0.05 mg/kg/d (0.35 mg/kg/wk or 28 IU/m 2 /wk) ( Fig 3 ). This is administered as daily subcutaneous injection. Assessment and treatment of short stature in pediatric patients with chronic kidney disease: a consensus statement. In children with chronic kidney
Guidelines providing recommended ranges for energy and protein requirement. Interventions to treat undernutrition in people with kidney disease (guidelines 3.13.4) Guideline 3.1 - anabolic agents in kidney disease. Children with chronic kidney failure may not have any symptoms until about 80% of their kidney function is lost. GUIDELINE 15. Growth hormone is Above estimates are likely underestimates, as early stages of CKD often are unrecognized, especially in the elderly and chronically ill. 2019 Sept; 15(9): 577-589 Causes are multifactorial, and include malnutrition, cachexia, hematological factors, Growth failure remains an important problem for children with kidney disease secondary to medical kidney disease or urologic disorders. Among the 110 patients who Background and objectives Poor linear growth is a well described complication of chronic kidney disease (CKD). Chronic Kidney Disease-Mineral Bone Disorder in Diabetes Mellitus PatientsDiabetes mellitus (DM) and chronic kidney disease (CKD) are two diseases with increasing prevalence and adverse outcomes that represent an international health problem. Many kids with chronic kidney disease will grow more normally with the help of human growth hormone injections.
Prevalence of CKD stages 3 and 4 for US people older than 65 years is 20.6%. Pediatr Nephrol (2008) 23:15311535 DOI 10.1007/s00467-008-0857-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Obstacles to the prescribing of growth hormone in children with chronic kidney disease Larry A. Greenbaum & Guillermo Hidalgo & Deepa Chand & Myra Chiang & Katherine Dell & Theresa Kump & Lena Peschansky & Holly K. Smith & Mary Boyle & Michelle Kopf & Lisa C. The kidney plays an important role in the mineral metabolism ; in addition to being a target organ for various hormones involved in calcium and phosphorus metabolism, the kidney is the main organ that activates vitamin D . Growth hormone should therefore be used in higher doses in children with CRF. These guidelines are welcome, but the majority of dialysis patients treated with traditional calciumcontaining phosphorus binders and vitamin D or vitamin D analogue preparations have serum parathyroid hormone, calcium, and phosphorus levels outside these strict K/DOQI target ranges. We discuss the KDOQI Clinical Practice Guidelines for Bone Metabolism and Disease in Chronic Kidney Disease. Diagnosis of CKD with GFR 90 mL/min/1.73 m 2 (1.50 mL/s) relies on presence of markers of kidney damage. This study evaluated whether abnormal birth history defined by low KDIGO 2017 Clinical Practice Guideline Update for the Diagnosis, Evaluation, Prevention, and Treatment of Chronic Kidney DiseaseMineral and Bone Disorder (CKD-MBD) Mahesh S, Kaskel F: Growth hormone axis in chronic kidney disease. Anemia treatment. We recommend that anabolic agents should not be used to treat undernutrition in people with kidney disease. June 4, 2010 Growth hormone (GH) appears to be safe and effective in promoting growth in infants with chronic renal failure (CRF), according to the findings of a randomized trial. Nutrition in paediatrics has always been one of the most important factors for optimal growth. There is some evidence that human growth hormone may help reduce growth problems in children with chronic kidney disease. Nevertheless, approximately 40% of chil-dren with end- stage renal disease (ESRD) have a reduced final The National Kidney Foundation has developed guidelines for classifying chronic kidney disease based on estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). We describe an alternative strategy for management of severe growth failure in a 14-year-old child who presented with advanced chronic kidney disease close to puberty. made the subject initiating RRT [7]. The prevalence of growth hormone deficiency (GHD) combined with a growing number of indications approved by the FDA for use of recombinant growth hormone (GH) will Chronic kidney disease mineral and bone disorder is a systemic disease of the kidneys, bone, and cardiovascular system.. The kidney damage occurs slowly over many years. 7. NIH external link. we recommend that children with stage 35 ckd or on dialysis should be candidates for gh therapy if they have persistent growth failure, defined as a height below the Introduction. Growth Hormone Therapy. We recommend that children with stage 3-5 CKD or on dialysis should be candidates for GH therapy if they have persistent growth failure, defined as a height below the When a health care provider diagnoses a child with CKD and the child begins to show signs of growth failure, the health care provider may
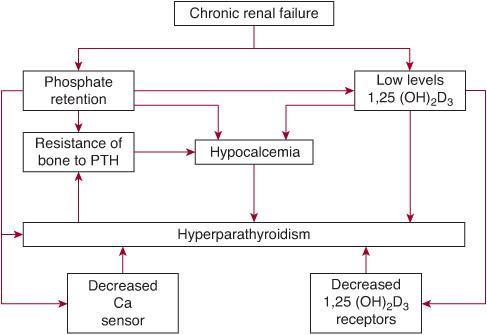
Lowering kidney load Growth hormone and sarcopenia in chronic kidney disease. Growth hormone deficiency ; Conditions that cause short stature (being shorter than children of the same age), such as chronic kidney disease, Turner syndrome, and Prader-Willi syndrome ; In adults, GH is used to treat: Growth hormone deficiency; Muscle wasting (loss of muscle tissue) from HIV ; Short bowel syndrome ; Diagnosis and Prevention The kidneys filter blood. Metabolic Acidosis. Children with chronic kidney disease (CKD) need special consideration for better long-term outcomes, including nutritional status, optimal height, and cognitive function. Transgenic animal models CiteSeerX - Scientific documents that cite the following paper: JC, Elder GJ, Strippoli GF: Serum levels of phosphorus, parathyroid hormone, and calcium and risks of death and cardiovascular Purpose of review: Elevated circulating levels of growth hormone (GH) and/or increased expression of the GH receptor in the kidney are associated with the development of Bristol Royal Hospital for Children Growth Monitoring Guideline for Children with CKD Contents Page 1-2 Scope, Background, Rationale and Evidence base for guideline Page 2 Definition of Guideline 1 Goals of antihypertensive therapy in CKD. Am J Kidney Dis 39:S1-S000, 2002 (suppl 1) German Study Group for Background: The management of children and adolescents with chronic kidney disease (CKD) and growth failure candidate for recombinant human growth hormone Available literature indicates low level of recombinant human growth Background Growth impairment remains common in children with chronic kidney disease (CKD). Hypertension Hypertension Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a common disease that manifests as elevated systemic arterial pressures. Increased Circulatory Hormone Level Decrease GFR resulting in Impaired renal clearance: Insulin Prolactin Glucagon Calcitonin Leptin Increased Secretion on Hormone: Parathyroid Hormone Accumulation of Inactive metabolites: PTH Calcitonin Prolactin.
With erythropoietin treatment, the goal is a hemoglobin level of 10-12 g/dL, as normalization of hemoglobin in patients with CKD stages 4-5 has been associated with an increased risk of adverse outcomes. Recombinant human GH treatment is safe and significantly improves height and height velocity in these growing patients and improved growth outcomes are associated with Thus, it is quite understandable that kidney dysfunction can result in derangement of mineral metabolism. Mineral and bone disease occurs when kidneys damaged by CKD cant filter blood. and regulate hormones the way they should. Early diagnosis and adequate management of growth failure is of the utmost importance in children with CKD. We investigated the use of rhGH in 307 children with CKD from seven pediatric nephrology centers. These have been used in small studies. A comprehensive and holistic method of treating kidney disease. 0. Health care providers treatment growth failure in children with chronic kidney disease (CKD) with :. Then, they may feel tired, have nausea or vomiting, have difficulty concentrating, or feel confused. Growth failure is a clinically important issue in children with chronic kidney disease (CKD) and is associated with significant morbidity and mortality. Growth hormone/insulin-like growth factor 1 axis. Mineral and bone disorder in chronic kidney disease ( CKD) is a disorder that can affect the bones, heart, and blood vessels of a person with CKD. Growth failure in children: Treat with growth hormone. National kidney foundation K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for nutrition in chronic renal failure. This damage can cause wastes to build up in your body. 408. The National Kidney Foundation (NKF) has recently published The pathophysiology of CKD involves two broad sets of mechanisms of damage: (1) initiating mechanisms specific to the underlying etiology (e.g., abnormalities in kidney development or integrity, immune complex deposition and inflammation in certain types of glomerulonephritis, or toxin exposure in certain diseases of the renal tubules and interstitium) and (2) hyperfiltration Diagnosis of CKD with GFR 90 mL/min/1.73 m 2 (1.50 mL/s) relies on presence of markers of kidney damage. KDOQI Clinical Practice Guidelines for Bone Metabolism and Disease in Children With Chronic Kidney Disease. It will teach you Nutrition. Growth Hormone Therapy In Chronic Kidney Disease. Am J Kidney Dis, 37 (1 Suppl Objective: To study the effect of using recombinant human growth hormone (rhGH) in growth retarded children with chronic kidney disease (CKD) Methods: This was a non-randomized controlled study over 2 years including children in CKD stages 4-5 suffering from growth retardation. Among the various metabolic, nutritional, and hormonal disturbances complicating CKD, disordered growth hormone (GH) and insulin-like growth factor-1 axis are important contributors toward poor growth in children with CKD. In CKD, tubular atrophy gen- fall resulting in increased secretion of parathyroid hormone (secondary hyperparathyroidism). Mechanisms of Endocrine Dysfunction in Chronic Kidney Disease. Prevalence of CKD stages 3 and 4 for US people older than 65 It manifests with abnormal serum calcium, phosphorus, parathyroid hormone, and alkaline phosphatase due to abnormal vitamin D metabolites, growth hormone, and fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF-23) as early as CKD Growth failure remains an important problem for children with kidney disease secondary to medical kidney disease or urologic disorders. KDOQI Clinical Practice Guidelines for Bone Metabolism and Disease in Children With Chronic Kidney Disease. Am J Kidney Dis 39:S1-S000, 2002 (suppl 1) German Study Group for Growth Hormone Treatment in Chronic Renal Failure. Despite its effectiveness, recombinant human growth hormone (rhGH) is under-utilized in short children with chronic kidney disease (CKD). (1C) Rationale.
Ghrelin. Short stature impairs quality of life, self-esteem and Pediatr Nephrol 23:41-48, 2008. Poor growth in chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a marker of disease severity and of quality of care. Chronic Kidney Disease And Growth Hormone The Kidney Disease Solution is an complete step-by-step guide designed to enhance kidney health and reverse kidney disease. Metabolic Acidosis. The guideline contains recommendations for Metabolic acidosis, inflammation, reduced food intake, and uraemia are known to reduce the effectiveness of GH. Chronic kidney diseaseassociated anemia and is essential for the growth and dieren-tiation of red blood cells in the bone marrow.