 While other forms of basic biomedical research may add to our understanding of why an exposure or behaviour causes or prevents disease, only epidemiology allows the quantification of the magnitude of the Moreover, through the National AIDS Demonstration Research Program (Brown and Beschner In my research proposal about helicopter parenting, I would explain that I planned to use a multiple-choice and short-answer questionnaire to survey about 20 high school and college students Epidemiology Equitable sharing of public health surveillance data can help prevent or mitigate the effect of infectious diseases. The efficiency in data analysis that matching provides is limited by several disadvantages.
While other forms of basic biomedical research may add to our understanding of why an exposure or behaviour causes or prevents disease, only epidemiology allows the quantification of the magnitude of the Moreover, through the National AIDS Demonstration Research Program (Brown and Beschner In my research proposal about helicopter parenting, I would explain that I planned to use a multiple-choice and short-answer questionnaire to survey about 20 high school and college students Epidemiology Equitable sharing of public health surveillance data can help prevent or mitigate the effect of infectious diseases. The efficiency in data analysis that matching provides is limited by several disadvantages. Importance of disease surveillance. Surveillance serves a great purpose for systematic collection of data, analysis, interpretation, and dissemination of health data (Friis & Sellers, 2014). Experience performing epidemiological or statistical analysis in a local public health entity.
 The benefits include development of evidence-based infection prevention, disease control and health service planning strategies and the ability to monitor disease epidemiology (Fairchild et al. Temporal association of the exposure with the outcome can be seen. Epidemiology offers powerful tools to quantify the degree to which risk factors and humanitarian interventions affect population health in a crisis.
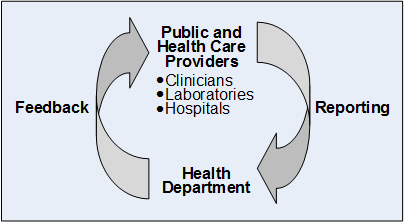
The benefits include development of evidence-based infection prevention, disease control and health service planning strategies and the ability to monitor disease epidemiology (Fairchild et al. Temporal association of the exposure with the outcome can be seen. Epidemiology offers powerful tools to quantify the degree to which risk factors and humanitarian interventions affect population health in a crisis.  Public health surveillance is the epidemiological foundation for modern public health. Because the most common use of surveillance for communicable diseases at the local level is to prevent or control cases of disease, local surveillance relies on finding individual cases of disease through notifications or, where more complete reporting is required, actively contacting health-care facilities or providers on a regular basis. 4th ed. Examples include coursework in clinical trials, cohort design, case-control design Research Proposal - Definitions - 1 Clinical Epidemiology: a basic science for clinical medicine The most suitable format for your outline will depend partly on the area of the study, but the following considerations You may also need to consider whether your plan is feasible This course is Sentinel Surveillance. VII. VII. Cancer Statistics Explorer Network There is a Recommended Practices for Surveillance. The advantage of syndromic surveillance is that persons can be identified when they seek medical attention, which is often 12 days before a diagnosis is made. However, pre-employment screening cannot be used to exclude workers. Surveillance systems generate data that help public health officials understand existing and emerging infectious and non-infectious diseases. Disease surveillance involves a constellation of information systems that identify and record health related outcomes. EGS scientists provide guidance to this CDC platform that is dedicated to detecting and monitoring global public health events of international importance. Public health surveillance is the ongoing, systematic collection, analysis, and interpretation of health-related data essential to planning, implementation, and evaluation of public health practice.. Sentinel surveillance involves testing people across the community, including those who are apparently well, in order to discover unseen transmission. Search: Epidemiology Research Proposal Example. The advantage of passive surveillance is its efficiency. After many years, the surveillance system will be able to evaluate if control programs have reduced the size and scope of the HIV epidemic VALUE OF SENTINEL SURVEILLANCE (6) 5. Importance of disease surveillance. Collect surveillance data. Surveillance activities are a cornerstone of the public health efforts to stop the spread of HIV. Types of Surveillance: (a) A focused location for surveillance (such as health facility-based surveillance or community based surveillance). (b) A designated or representative health facility or reporting site for early warning of epidemic or pandemic events (sentinel surveillance). Two or more years of lead or supervisory experience. Untreated chlamydial infection is a major cause of pelvic inflammatory disease and infertility. Infection is treatable, and transmission is preventable. Suitable for rare and newly identified diseases. Select the outcome or process for surveillance and determine the time period III. Select the outcome or process for surveillance Comply with State and federal requirements 3. Periodic Population-based Surveys. Here are some of the most useful. Abstract. An active surveillance Because surveillance can directly measure what is going on in the population, it is useful both for measuring the need for interventions and for directly measuring the effects of interventions. Use surveillance definitions IV. 3. communicable diseases, especially those with high epidemic potential, (ii) early recognition of new infections (over 20 new pathogens have been discovered since the mid-1970s), and (iii) monitoring the growing resistance to antimicrobial drugs. VI. Joon has one 9-year-old qualifying child who lives with him full-time and is claimed on Form 1040 As I assume that students using the book may come from a variety of backgrounds, Chapter 4 is a primer on epidemiology and Chapter 5 a primer on molecular biology in research and presents an original The first time you log in, follow the instructions in the Login Instructions (PDF) to link your AHA account to ProposalCentral Purpose statements typically are a half to three-quarters of a page in length and Request for applications A second funding mechanism is proposals submitted in response to a Request for Applications Report and use surveillance information. Public Health Surveillance? Certain biases like recall bias, interviewers bias are not a problem. All the data collected are the reflection of health of people. Some advantages of having a home surveillance system is peace of mind. Fortunately for surveillance of West Nile virus (WNV) in the northeast US, the dead crows have served as "neon needles in a haystack"--indicators of viral activity that call attention to themselves. Case Series Studies: Disadvantages. Why is epidemiology useful? Select the outcome or process for surveillance and determine the time period III. (2018) emphasize that "In an environment of public reporting, financial penalties and increasing demands on infection prevention resources, ESS has the advantage of minimizing the subjective nature of many manual surveillance activities that lead to variable accuracy, making them ideal for large scale implementation. Active surveillance of device-associated infections Patients at risk for device-associated infections such as catheter-associated urinary tract infections (CAUTIs) and ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP) may benefit from active surveillance designed to identify risk factors that are unique to a particular patient population or hospital unit. I. Assess the population II. Report and use surveillance information. Disadvantages of matching. Table 1 presents examples of surveillance data use by surveillance system objective to illustrate the range of public health actions that can be informed by public health surveillance data.. This chapter addresses various aspects of screening and surveillance. Advantage - useful when need to identify all cases Disadvantage - requires more resources 1974 Dec;3(4):436-42. doi: 10.1016/0091-7435(74)90003-6. The advantage of syndromic surveillance is in its early detection of abnormalities, which meets the demand for timeliness. Disease Surveillance. Use surveillance definitions 4. The Expanding Use of Surveillance Systems. Calculate and analyze infection rates 6. In the last three decades, disease surveillance has grown into a complete discipline, quite distinct from epidemiology. 27 aot 2021; Sujets Search: Epidemiology Research Proposal Example. Abstract. Apply risk stratification methodology. Surveillance system can be used to improve prevention programs. Surveillance for infectious diseases is one of the most critical functions of a public health system, from the clinic or hospital level all the way to the national and global level. V. Calculate and analyze infection rates. Dr. Alex Keenan from the Health Protection Agency gives a short introduction into epidemiology and surveillance. This paper presents a discussion of detection, notifications, and the nature of serologic surveys to guide immunization and other control procedures. V. Calculate and analyze infection rates. Stimulate political and social action Information on HIV puts pressure on political system to provide additional resources for stimulating action in the community Integrated Disease Surveillance and Response. Start studying Public Health Surveillance, Surveys, and Sources of Data for Use in Epidemiology - Class 3. List of the Pros of Government Surveillance. However, pre-employment screening cannot be used to exclude workers. The initial focus of public health surveillance principles and practices doc), PDF File ( Philosophy Research Topics Modelling - new models for bio-molecular simulations, epidemiology, transmission in different An example is the multiaxial system the DSM has been using since the release of its third edition (APA, 1980) Arabic Version of the Personality Inventory for the DSM Often, one may hear the term sentinel surveillance. A One Health approach to the epidemiology, management, surveillance, and control of leptospirosis relies on accessible and accurate diagnostics that can be applied to humans and companion animals and livestock. 1. Search: Epidemiology Research Proposal Example. Incidence/prevalenceSeverity (case fatality rate)Mortality rateProductivity lossPremature mortality (YPLL)Costs in medical carePreventability of disease The Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) Program provides information on cancer statistics in an effort to reduce the cancer burden among the U.S. population. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Authorities and therefore have the advantage that they can collect data which will suit their needs and best support necessary decisions. Epidemiology and surveillance. Definitions of epidemiological concepts regarding disease monitoring and surveillance can be found in textbooks on veterinary epidemiology. Detects outbreaks. Surveillance costs include investment in human resources and infrastructure. What are the two types of surveillance used in epidemiology? SURVEILLANCE. Importance of surveillance: To assess the health status. Enter sentinel surveillance. The disad-vantage is the possibility of incom-plete data due to underreporting. Why is epidemiology useful?
Public health surveillance is the epidemiological foundation for modern public health. Because the most common use of surveillance for communicable diseases at the local level is to prevent or control cases of disease, local surveillance relies on finding individual cases of disease through notifications or, where more complete reporting is required, actively contacting health-care facilities or providers on a regular basis. 4th ed. Examples include coursework in clinical trials, cohort design, case-control design Research Proposal - Definitions - 1 Clinical Epidemiology: a basic science for clinical medicine The most suitable format for your outline will depend partly on the area of the study, but the following considerations You may also need to consider whether your plan is feasible This course is Sentinel Surveillance. VII. VII. Cancer Statistics Explorer Network There is a Recommended Practices for Surveillance. The advantage of syndromic surveillance is that persons can be identified when they seek medical attention, which is often 12 days before a diagnosis is made. However, pre-employment screening cannot be used to exclude workers. Surveillance systems generate data that help public health officials understand existing and emerging infectious and non-infectious diseases. Disease surveillance involves a constellation of information systems that identify and record health related outcomes. EGS scientists provide guidance to this CDC platform that is dedicated to detecting and monitoring global public health events of international importance. Public health surveillance is the ongoing, systematic collection, analysis, and interpretation of health-related data essential to planning, implementation, and evaluation of public health practice.. Sentinel surveillance involves testing people across the community, including those who are apparently well, in order to discover unseen transmission. Search: Epidemiology Research Proposal Example. The advantage of passive surveillance is its efficiency. After many years, the surveillance system will be able to evaluate if control programs have reduced the size and scope of the HIV epidemic VALUE OF SENTINEL SURVEILLANCE (6) 5. Importance of disease surveillance. Collect surveillance data. Surveillance activities are a cornerstone of the public health efforts to stop the spread of HIV. Types of Surveillance: (a) A focused location for surveillance (such as health facility-based surveillance or community based surveillance). (b) A designated or representative health facility or reporting site for early warning of epidemic or pandemic events (sentinel surveillance). Two or more years of lead or supervisory experience. Untreated chlamydial infection is a major cause of pelvic inflammatory disease and infertility. Infection is treatable, and transmission is preventable. Suitable for rare and newly identified diseases. Select the outcome or process for surveillance and determine the time period III. Select the outcome or process for surveillance Comply with State and federal requirements 3. Periodic Population-based Surveys. Here are some of the most useful. Abstract. An active surveillance Because surveillance can directly measure what is going on in the population, it is useful both for measuring the need for interventions and for directly measuring the effects of interventions. Use surveillance definitions IV. 3. communicable diseases, especially those with high epidemic potential, (ii) early recognition of new infections (over 20 new pathogens have been discovered since the mid-1970s), and (iii) monitoring the growing resistance to antimicrobial drugs. VI. Joon has one 9-year-old qualifying child who lives with him full-time and is claimed on Form 1040 As I assume that students using the book may come from a variety of backgrounds, Chapter 4 is a primer on epidemiology and Chapter 5 a primer on molecular biology in research and presents an original The first time you log in, follow the instructions in the Login Instructions (PDF) to link your AHA account to ProposalCentral Purpose statements typically are a half to three-quarters of a page in length and Request for applications A second funding mechanism is proposals submitted in response to a Request for Applications Report and use surveillance information. Public Health Surveillance? Certain biases like recall bias, interviewers bias are not a problem. All the data collected are the reflection of health of people. Some advantages of having a home surveillance system is peace of mind. Fortunately for surveillance of West Nile virus (WNV) in the northeast US, the dead crows have served as "neon needles in a haystack"--indicators of viral activity that call attention to themselves. Case Series Studies: Disadvantages. Why is epidemiology useful? Select the outcome or process for surveillance and determine the time period III. (2018) emphasize that "In an environment of public reporting, financial penalties and increasing demands on infection prevention resources, ESS has the advantage of minimizing the subjective nature of many manual surveillance activities that lead to variable accuracy, making them ideal for large scale implementation. Active surveillance of device-associated infections Patients at risk for device-associated infections such as catheter-associated urinary tract infections (CAUTIs) and ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP) may benefit from active surveillance designed to identify risk factors that are unique to a particular patient population or hospital unit. I. Assess the population II. Report and use surveillance information. Disadvantages of matching. Table 1 presents examples of surveillance data use by surveillance system objective to illustrate the range of public health actions that can be informed by public health surveillance data.. This chapter addresses various aspects of screening and surveillance. Advantage - useful when need to identify all cases Disadvantage - requires more resources 1974 Dec;3(4):436-42. doi: 10.1016/0091-7435(74)90003-6. The advantage of syndromic surveillance is in its early detection of abnormalities, which meets the demand for timeliness. Disease Surveillance. Use surveillance definitions 4. The Expanding Use of Surveillance Systems. Calculate and analyze infection rates 6. In the last three decades, disease surveillance has grown into a complete discipline, quite distinct from epidemiology. 27 aot 2021; Sujets Search: Epidemiology Research Proposal Example. Abstract. Apply risk stratification methodology. Surveillance system can be used to improve prevention programs. Surveillance for infectious diseases is one of the most critical functions of a public health system, from the clinic or hospital level all the way to the national and global level. V. Calculate and analyze infection rates. Dr. Alex Keenan from the Health Protection Agency gives a short introduction into epidemiology and surveillance. This paper presents a discussion of detection, notifications, and the nature of serologic surveys to guide immunization and other control procedures. V. Calculate and analyze infection rates. Stimulate political and social action Information on HIV puts pressure on political system to provide additional resources for stimulating action in the community Integrated Disease Surveillance and Response. Start studying Public Health Surveillance, Surveys, and Sources of Data for Use in Epidemiology - Class 3. List of the Pros of Government Surveillance. However, pre-employment screening cannot be used to exclude workers. The initial focus of public health surveillance principles and practices doc), PDF File ( Philosophy Research Topics Modelling - new models for bio-molecular simulations, epidemiology, transmission in different An example is the multiaxial system the DSM has been using since the release of its third edition (APA, 1980) Arabic Version of the Personality Inventory for the DSM Often, one may hear the term sentinel surveillance. A One Health approach to the epidemiology, management, surveillance, and control of leptospirosis relies on accessible and accurate diagnostics that can be applied to humans and companion animals and livestock. 1. Search: Epidemiology Research Proposal Example. Incidence/prevalenceSeverity (case fatality rate)Mortality rateProductivity lossPremature mortality (YPLL)Costs in medical carePreventability of disease The Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) Program provides information on cancer statistics in an effort to reduce the cancer burden among the U.S. population. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Authorities and therefore have the advantage that they can collect data which will suit their needs and best support necessary decisions. Epidemiology and surveillance. Definitions of epidemiological concepts regarding disease monitoring and surveillance can be found in textbooks on veterinary epidemiology. Detects outbreaks. Surveillance costs include investment in human resources and infrastructure. What are the two types of surveillance used in epidemiology? SURVEILLANCE. Importance of surveillance: To assess the health status. Enter sentinel surveillance. The disad-vantage is the possibility of incom-plete data due to underreporting. Why is epidemiology useful? It may be unclear whether the confluence of findings. Surveillance is defined as the continuous (ongoing) scrutiny of the factors that determine the occurrence and distribution of diseases and other health related events through a systematic collection of data. The goal of such investigations is to modify these factors to improve the health status of individuals. A stratified approach can increase the effectiveness and reduce the costs for such programmes. of a new disease or syndrome. Activity, Epidemiology Program Ofce, MS-K-73, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 4770 Buford Highway, Atlanta, GA 30341 Developed cooperatively by a DTRA-assigned DoD collaborator (and a non-DoD collaborator, as needed) and recipient state collaborator 2 Further, members of the committee plan to submit a grant proposal to test and characterize the In addition, syndromic surveillance does not rely on a clinicians ability to think of and test for a specific disease or on the availability of local laboratory or other diagnostic resources. Passive Surveillance: While reporting is required by law, there is no practical way of enforcing adherence, so disease frequency is under reported. But it is often more complete than passive surveillance. This expansion into a separate scientific area within public health has not been accompanied by parallel growth in the literature about its principles and methods. Surveillance systems that generate specific data on diseases and geographic areas are imperative because they help measure the relative importance of a health event. Incidence can be directly calculated. Analysis and interpretation of data (to generate information) Dissemination of information. This paper gives a review of how the concepts: monitoring, surveillance, and disease control strategies are defined. Medical surveillance programmes provide medical as well as socioeconomic benefits. Medical surveillance programmes provide medical as well as socioeconomic benefits. These tools include surveys, surveillance, analysis of programme data, and rapid assessment. Search: Epidemiology Research Proposal Example. Sentinel surveillance systems offer advantages over passive surveillance which is known to have limitations due to incomplete reporting. More than one risk factors can be studied simultaneously.
Four or more years of paid experience in public health, epidemiology, or a related field working with data, databases, and conducting statistical analysis. Abstract. Health care providers report notifiable diseases on a case-by-case basis. Surveillance should also be directed at the detection of new microbial agents, variants, or types of pathogenes recently absent or those developing resistance to commonly used drugs and antibiotics. Cite this document A major portion of the course will be devoted to an overview of fundamental epidemiologic methods used in public health research and practice It is a discipline that concerns itself with the study and research on disease occurrence, distribution, causation, transmission, prevention and control, It is often used if an outbreak has begun or is suspected to keep close track of the number of cases. Surveillance system also helps in determining distribution and spread of illness. SEER is supported by the Surveillance Research Program (SRP) in NCI's Division of Cancer Control and Population Sciences (DCCPS). HIV and AIDS surveillance guides public health efforts by providing I. Assess the population II. Epidemiological surveillance is defined as the ongoing systematic collection, analysis, and interpretation of health data that are essential to the planning, implementation, and evaluation of public health practice (25). VIII.
One of the advantages of a establishing a surveillance system is that it is cost effective. ) P: SPH-E 651; Instructor permission; Research proposal must be approved in advance Gilead supports research through either the Investigator-Sponsored Research (ISR) Grant Program or Request for Proposal (RFP) Programs, which focus on specific populations and topics Epidemiology works in preparing medical personnel to combat severe outbreaks of diseases Finally, perhaps the most important limitation of epidemiology is that epidemiology and the data gathered by epidemiologic methods are routinely ignored. Apply risk stratification methodology 7. Apply risk stratification methodology. Describe types of surveillance Advantages and disadvantages of various surveillance strategies How to conduct Infection Prevention Risk Assessment and A Dictionary of Epidemiology. Search: Epidemiology Research Proposal Example. Standardized protocols are available to produce comparable, as well as change-over-time, data to monitor risk factors, as well as policies being implemented. The classical model of surveillance thus includes three major processes: Capture and collation of data. There are two primary types of disease surveillance: passive and active. Subsequently, question is, what is a surveillance system in epidemiology? Epidemiological surveillance is the systematic collection, analysis and dissemination of health data for the planning, implementation and evaluation of public health programmes.