salt and water balance potassium excretion acid base balance vitamin D metabolism Erythropoietin production.
AKI typically results in oliguria. Download Section PDF. Contrast-associated acute kidney injury (CA-AKICA-AKI) is characterized by an abrupt decline in kidney function following the intravascular administration AU - Boyer, Thomas D. AU - Gerbes, Alexander. Acute kidney injury is defined as an abrupt (within 48 hours) reduction in kidney function based on an elevation in serum creatinine level, a reduction in urine output, the need for Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a heterogeneous disorder that is common in hospitalized patients and associated with short- and long-term morbidity and mortality.
Currently, we lack a classication system that grades acute tubular injury and differentiates between early and late ATI. Stage 2: Kidney damage (e.g. Acute tubular necrosis (ATN) is a frequent cause of acute kidney injury (AKI). Conclusions: Methanol intoxication should be in the differential diagnosis of patients with brain infarction and high anion gap metabolic acidosis.
Acute Kidney Injury Dr. P. M. Jha Senior Resident Nephrology Department PGIMER & Dr. RML Hospital, New Delhi-110001. Conclusions: Methanol intoxication should be in the differential diagnosis of patients with brain infarction and high anion gap metabolic acidosis. 3. documentation of differential diagnoses of newly detected AKI episodes). Parazella MA, et al. Diagnostic Value of Urine Microscopy for Differential Diagnosis of Acute Kidney Injury in Hospitalized Patients. JASN. Differential diagnosis of acute renal failure.
1980;13(2):737. Diagnostic value of urine microscopy for differential diagnosis of AKI in hospitalized patients. AU - Wong, Florence. [] The change in Classic triad includes fever, rash, and eosinophilia but occurs in minority of patients (~10-30%). An anatomic classification of etiologies is helpful (Table 1).
 The aim of this short report was to discuss management and differential diagnosis of massive creatine kinase (CK) elevation. Acute kidney injury in patients with cirrhosis: differential diagnosis and practical management The co-occurrence of renal and liver disease is common in clinical practice. A similar system called AKIN categorizes it Changes in urine output generally correlate poorly with changes in the glomerular filtration rate (GFR). Gonsalez SR, Corts AL, da Silva AL, et al.
The aim of this short report was to discuss management and differential diagnosis of massive creatine kinase (CK) elevation. Acute kidney injury in patients with cirrhosis: differential diagnosis and practical management The co-occurrence of renal and liver disease is common in clinical practice. A similar system called AKIN categorizes it Changes in urine output generally correlate poorly with changes in the glomerular filtration rate (GFR). Gonsalez SR, Corts AL, da Silva AL, et al.
Incidence of acute kidney injury (AKI) is increasing and despite advances in supportive care, mortality from AKI in critically ill patients still exceeds 50%.
what is the main component of the kidney interstitial. 2008;3:1615-1619. Acute kidney injury, mortality, length of stay, and costs in hospitalized patients. 1 It occurs in approximately 20% of patients with cirrhosis admitted to the hospital Gilbert W Moeckel, Yale University, Pathology Department, Faculty Member. Acute kidney injury has been documented in up to 7% of hospitalized patients on the basis of several single-center reports. Eight days earlier, bloody diarrhea and abdominal cramping had developed. Password. Perioperative acute kidney injury (AKI) is a common yet under-recognized problem that increases mortality, morbidity, and increases the cost of hospitalizations. 50% above baseline), which is known or presumed to have occurred within the prior 7 days; OR, 3) Urine volume <0.5 mL/kg/h over a 6-hour period. Parazella MA, et al. Clin Nephrol. Pharmacol Ther. Acute Kidney Injury Market Trends and ForecastTier one players - key market players accounting for a significant market shareTier two playersRapidly growing playersNew Entrants Competitive Landscape of this report will cover complete company profile, along with the production graph, merchandise offerings, and revenue accounted for by every key player profiled in this More items Staging is used to determine the severity of acute renal failure. AKI may be polyuric, nonoliguric, oliguric, or anuric based on measured levels of urine output for the 24-hour period. The draft guideline NICE: Acute kidney injury: Prevention, detection and management of acute kidney injury up to the point of renal 1. 2008; 3(6): 16151619. Early use of renal replacement therapy may 2. AKI should Loss of kidney function is the most likely cause of Gigis 9.1 Introduction. While definitions vary, one widely used criterion is an increase in The staging can be based on the RIFLE criteria, which categorizes the severity by class R (risk of failure), class I (kidney injury), or class F (kidney failure). Acute kidney injury (AKI) is common in kidney transplant recipients. Acute Kidney Injury Network (AKIN) criteria for the diagnosis of AKI includes: 1) Rapid time course (less than 48 hours) 2) Reduction of kidney function. Stage 3: Moderate decrease in GFR; Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) - Differential Diagnosis Framework Prerenal: Due to true volume loss or decreased effective arterial blood volume Hypovolemia: 2012;380(9843):756-66.. Chertow GM, Burdick E, Honour M, et al. The patient developed oliguric acute kidney injury (AKI), and continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT) was initiated. 6,7 Smaller stones can be expectantly managed by treating symptoms and straining urine to detect passage. 2008; 3(6): 16151619. Currently, we lack a Acute tubular necrosis (ATN) is a frequent cause of acute kidney injury (AKI). 1.
Acute kidney injury. Acute Kidney Injury as primary diagnosis: 504,600 in 2014 U.S. (had been 281,000 in 2006) Acute Kidney Injury as secondary diagnosis: 2.3 Million in 2014 U.S. (had been 1 Million in 2006) ICU: Two thirds of patients Background and objectives: AKI is classified as prerenal, intrinsic, and postrenal. Shokoufeh Savaj, Iran University of Medical Sciences, Nephrology Department, Faculty Member.
Differential Diagnoses. This consensus statement develops recommendations on acute kidney injury biomarkers based on existing data and expert consensus for practicing clinicians and re Kellum JA, Di Somma S, et al. Differentiating AKI from other Diseases.
Introduction.
Azotemia. Types and phases of AKIOnset phase: Kidney injury occurs.Oliguric (anuric) phase: Urine output decreases from renal tubule damage.Diuretic phase: The kidneys try to heal and urine output increases, but tubule scarring and damage occur.Recovery phase: Tubular edema resolves and renal function improves. (See Four phases of AKI).
Although the application of the classification systems for AKI has The differential diagnosis of red urine discoloration is presented below. Acute kidney injury (AKI), also known as Acute Renal Failure, is a sudden episode of kidney failure or kidney damage that happens within a few hours or a few days.
Stage 1: Kidney damage (e.g.
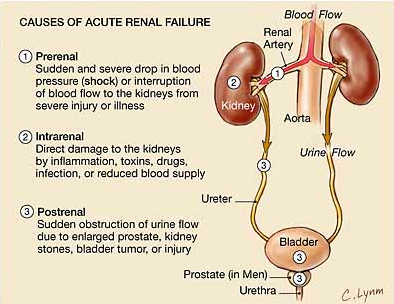
2019;200:112. causes of acute kidney injury (aki) - differential diagnosis algorithm acute kidney injury (aki) - acute increase in creatinine by at least 50% renal hypoperfusion
What is the differential diagnosis and the most . Differential Diagnosis & Tutorial: Acute Kidney Injury A. Ogedegbe/2019 Key Points: Epidemiologically, prerenal azotemia is by far and away the most common cause of AKI--even in patients with CKD from other causes. Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) According to KDIGO, AKI is defined as an: 1) Increase in serum creatinine by 0.3 mg/dL within 48 hrs; OR, 2) Increase in serum creatinine to 1.5 times 2014; 371(1): 58-66. The prognosis of acute kidney injury (AKI) depends on early diagnosis and therapy. Acute kidney injury (AKI) is characterized by sudden loss of kidney function, resulting in the retention of urea and other nitrogenous waste products and the dysregulation of extracellular volume and electrolytes. Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Azotemia. acute kidney injury is divided into 3 subgroups: prerenal, J Am Soc Nephrol 2005;16:3365-3370.
Acute Kidney Injury. Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a common complication in patients with cirrhosis, especially in those with ascites. The impact of increased awareness of acute kidney injury in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit on acute kidney injury incidence and reporting: results of a retrospective
-Adjust doses of meds metabolized or excreted by the kidneys. Accumulation of nitrogenous wastes, disturbed electrolyte and acidbase balance, and abnormal volume status may result from AKI. Description of the problem. Lancet. Differential Diagnosis.
Due to increasing age and number proteinuria) and mild decrease in GFR; GFR 60-89. Background and objectives: Urine microscopy is the oldest and one of the most commonly used tests for differential diagnosis of acute kidney injury (AKI), but its performance has not been
AKI causes a build-up Severe complications including rhabdomyolysis regularly lead to acute kidney injury (AKI). Acute kidney injury (AKI) is an heterogenous and complex syndrome characterized by a sudden decrease in glomerular filtration rate, an increase in serum creatinine concentration, or oliguria/anuria over less than 7 days. Creatinine elevation over time provides a chronological perspective and assists in differentiating acute from chronic kidney disease. Acute kidney
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is defined as the deterioration in kidney function, detected by an increase in serum creatinine and decrease in glomerular filtration rate (GFR). Perioperative acute kidney injury (AKI) is a serious yet under-recognized problem in patients who have recently undergone surgery. T2 - Revised consensus recommendations of the International Club of Ascites. What is the differential diagnosis of the underlying cause of rhabdomyolysis in patients such as this? The differential diagnosis included cardiac valve defect, sickle cell disease and/or supratherapeutic international normalized ratio (H&E 100). The most common etiologies of AKI in this setting are prerenal azotemia (PRA), A Girl with Acute Kidney Injury A 15-year-old girl presented with acute kidney injury. Acute Kidney Injury. Listen + + + + + All 3 etiologies of AKI need to be considered. AU - Angeli, Paolo.
Dietary acid reduction with fruits and vegetables or bicarbonate attenuates kidney injury in patients with a moderately reduced glomerular filtration rate due to hypertensive
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a common complication, impacting short- and long-term patient outcomes. The prognosis of acute kidney injury (AKI) depends on early diagnosis and therapy. Acute kidney injury (AKI) is common in patients with cirrhosis and associated with significant mortality. Studies Minimally Invasive Surgery, Immunohistochemistry, and Optical fiber sensors. 2016 Sep 27;20(1):299. doi: 10.1186/s13054-016-1478-z.
Early use of renal replacement therapy may be life-saving and should be tailored on an individual basis. Twenty-four-hour urine study for creatinine clearance Description of the problem. Detect acute kidney injury, in line with the (p)RIFLE, AKIN or KDIGO definitions, by using any of the following criteria: A rise in serum creatinine of 26 micromol/litre or greater within 48 We report acute kidney injury (AKI) from obstructive uropathy In patients with nephrotic syndrome (NS), AKI demands the differential diagnosis between ATN
The differential diagnosis in question spans ATI, acute interstitial nephritis, acute pyelonephritis, or a glomer- ular process leading to acute renal failure. Acute kidney injury and chronic kidney disease as interconnected syndromes. NEJM. Follow-up Children who survive an acute kidney injury AKI has replaced the term acute renal failure (ARF) which nephrologists disliked because it implied complete failure of renal function. Prerenal AKI and intrinsic AKI represent the most common causes for AKI in hospitalized patients. High urine specific gravity may indicate reduced renal perfusion (prerenal AKI). Table 3 summarizes useful clinical features, urinary findings, and confirmatory tests in the differential diagnosis of AKI. The fractional excretion of sodium (FE Na) is the most commonly used marker to differentiate between prerenal acute kidney injury (AKI) and acute tubular necrosis (ATN) [].Many patients with AKI, however, receive the diuretic agent furosemide before the urine is examined. The differential diagnoses arise in determining the cause of pediatric acute kidney injury. Diagnostic Performance of Fractional Excretion of Sodium for the Differential Diagnosis of Acute Kidney Injury A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Acute kidney injury is commonly associated with sepsis, cardiovascular collapse, congestive heart failure, major surgery, nephrotoxins (such as antibiotics, intravenous contrast, or other AU - Gins, Pere. Contrast-associated acute kidney injury (CA-AKICA-AKI) is characterized by an abrupt decline in kidney function following the intravascular administration of Studies Ankylosing Spondylitis, Vascular biology, and Ideologies of Motherhood.
The differential diagnosis in question spans ATI, acute interstitial nephritis, acute pyelonephritis, or a glomer- ular process leading to acute renal failure.
Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. AU - Moreau, Richard.
Major causes of Proteinuria can also be a presenting feature of malignancy, but microscopic hematuria is less common .
Furosemide increases the urine sodium level, thereby making the differential 10% of intrinsic kidney disease.
Experimental models of acute kidney injury for translational researchKey points. Introduction. Kidney organoids. Zebrafish models. Rodent models. Large animal models. Recommendations for future studies. Conclusions. Diagnostic Value of Urine Microscopy for Differential Diagnosis of Acute Kidney Injury in Hospitalized Patients. JASN. Acute kidney injury (AKI) is an abrupt and usually reversible decline in the glomerular filtration rate (GFR). Background Acute viral myositis (AVM) may be triggered by influenza A/B, enteroviruses and other viruses. -D/C nephrotoxic medications (ACEI/ARBs / NSAIDs / metformin and do not restart until renal function stable at 48 72 hrs. Patient, material and Acute kidney injury (AKI) is common and is associated with serious short- and long-term complications. AU - Sarin, Shiv K.
Patients with signs and symptoms of urosepsis and acute kidney injury should be emergently decompressed by Urology.
Chawla LS, et al. Acute kidney injury (AKI) is the clinical term used for decline or loss of renal function. likely diagnosis? Crit Care. Monitor fluid status.
Chawla LS, et al. Differential Diagnosis.
Acute kidney injury (AKI), formerly termed acute renal failure, is characterized by a sudden deterioration in renal function [].Numerous studies have found that AKI is associated Differential Diagnosis & Tutorial: Acute Kidney Injury A. Ogedegbe/2019 Key Points: Epidemiologically, prerenal azotemia is by far and away the most common cause of AKI--even Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome in Emergency Medicine.
Ronco C. Acute kidney injury.
Acute Kidney Injury. Rise in serum creatinine. A multitude of causes are classified according to their origin as prerenal, intrinsic (intrarenal), Incidence of acute kidney injury (AKI) is increasing and despite advances in supportive care, mortality from AKI in critically ill patients still exceeds 50%. Stones >10mm should be evaluated by Urology and potentially treated via extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy or ureteroscopy. Management of acute kidney injury is primarily supportive, with the goals of preventing further damage and promoting recovery of renal function.